Volume 25, Number 8—August 2019
Research
Natural Vertical Transmission of Zika Virus in Larval Aedes aegypti Populations, Morelos, Mexico
Figure 2
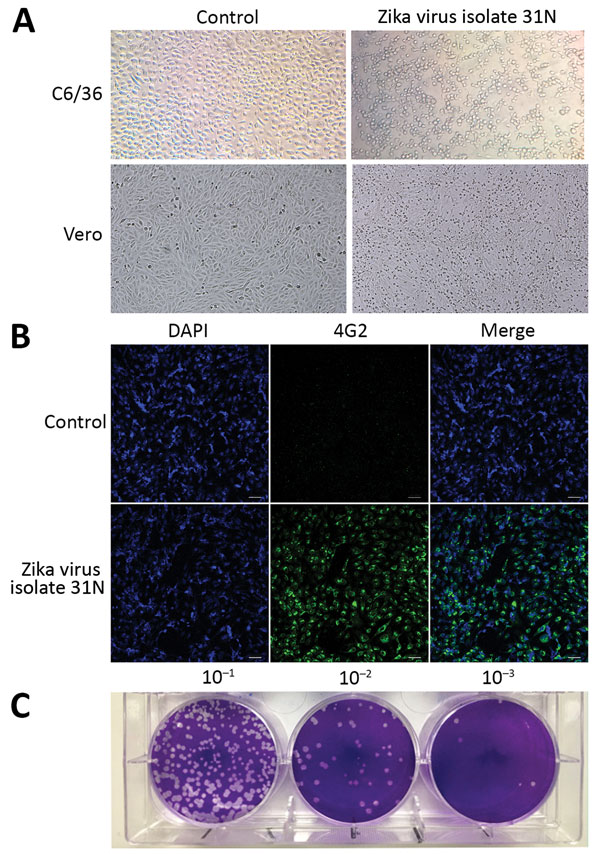
Figure 2. Phenotypic analysis of Zika virus isolate 31N from an Aedes aegypti larval pool, Jojutla, Morelos, Mexico. A) Cytopathic effect of the Zika virus isolate 31N in C6/36 and Vero cells. The left panel shows mock infected cells. Original magnification ×20. B) Infected Vero cells with Zika virus isolate 31N at a multiplicity of infection of 0.1 and mock infected cells. Nuclei are stained in blue (DAPI), and the envelope protein is stained in green (4G2). Original magnification ×20. C) Plaque assay of Zika virus isolate 31N in Vero cells. Serial decimal dilutions of Zika virus isolate 31N are depicted.
Page created: July 16, 2019
Page updated: July 16, 2019
Page reviewed: July 16, 2019
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.