Volume 25, Number 8—August 2019
Dispatch
Lethal Encephalitis in Seals with Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection, China, 2017
Figure 1
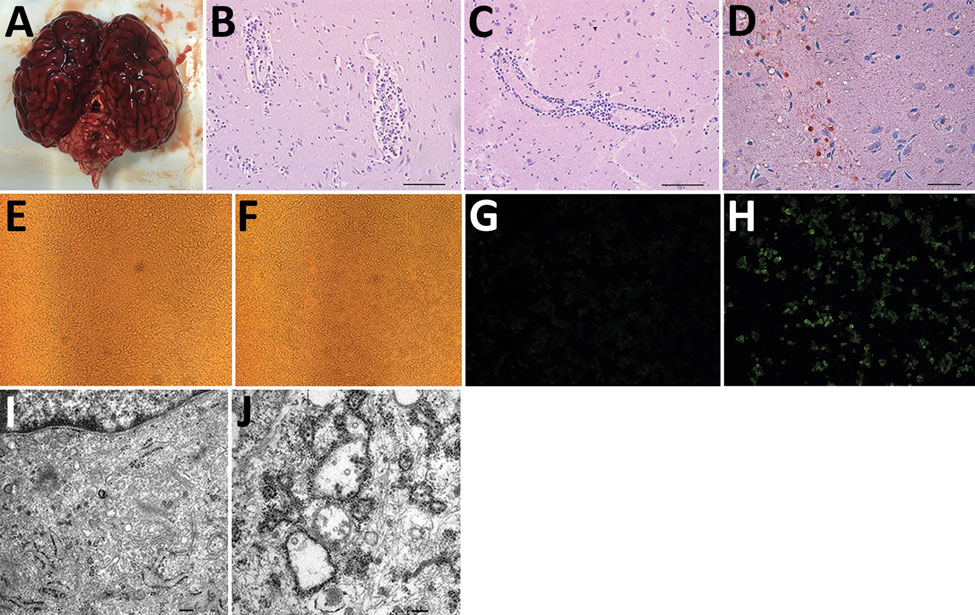
Figure 1. Pathologic examination and virus culturing of brain tissue samples from 2 seals with lethal encephalitis infected with Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), China, 2017. A) Hemorrhaging seal brain. B) Histochemical staining of a glial nodule in the cerebrum showing lymphocyte infiltration around small blood vessels. Scale bar represents 50 μm. C) Histochemical staining of tissue showing coalescing nonsuppurative encephalitis with neuronal degeneration and perivascular cuffing. Scale bar represents 50 μm. D) Immunohistochemical staining of tissue with anti-JEV polyclonal mouse serum showing JEV antigen. Scale bar represents 20 μm. E–H) Baby hamster kidney cell line BHK-21 incubated with (F, H) and without (E, G) JEV Seal-Anheal-2017 (i.e., brain homogenate supernatant from infected seals passaged through BHK-21 cells 4 times) fluorescently stained by using anti-JEV polyclonal mouse serum (G, H). Cells incubated with the fourth passage of brain homogenate demonstrated cytopathic effect (F) and fluorescence (H), indicating the presence of JEV antigen. Original magnification ×200. I, J) Electron microscopic images of BHK-21 cells not infected (I) and infected (J) with Seal-Anheal-2017. Many mature virions and proliferative vesicles were observed in the endoplasmic reticulum of JEV-infected cells (J). Scale bars represent 0.2 μm.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.