Volume 26, Number 12—December 2020
Dispatch
Shedding of Marburg Virus in Naturally Infected Egyptian Rousette Bats, South Africa, 2017
Figure 1
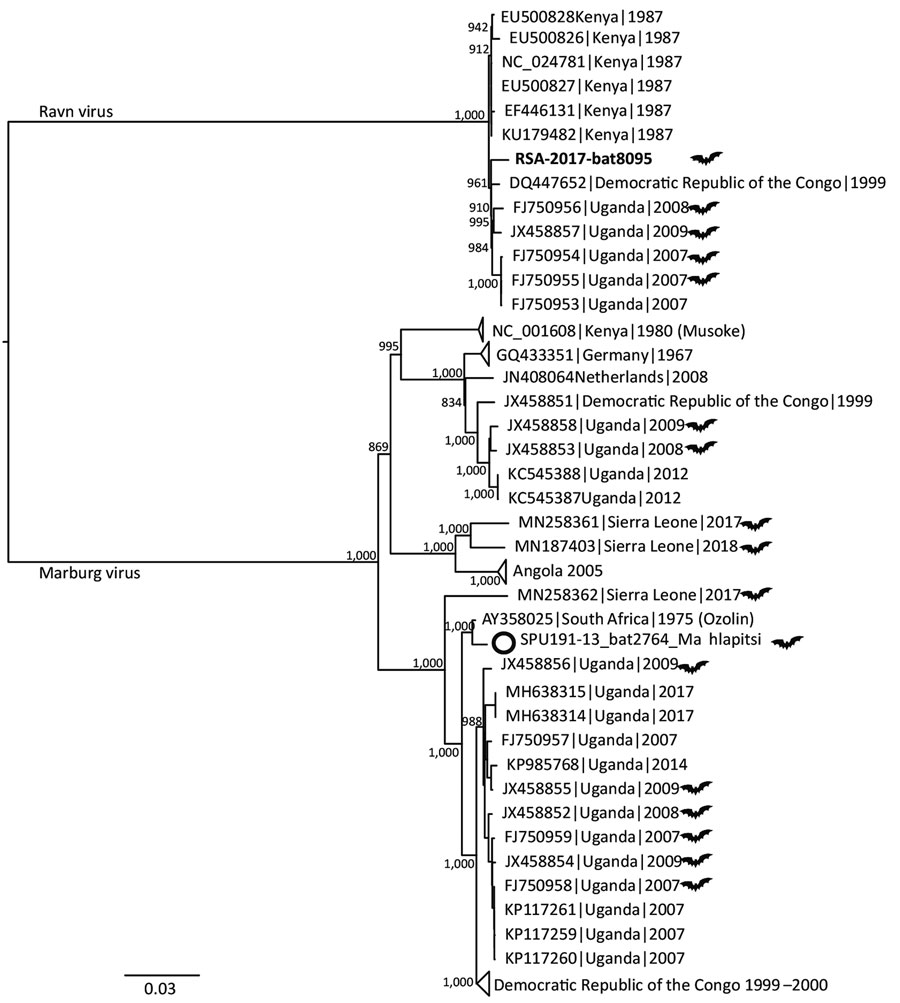
Figure 1. Midpoint-rooted, maximum-likelihood phylogeny of complete and near-complete MARV and RAVV genomes. Phylogenetic tree shows evolutionary relationships of marburgvirus detected in a rectal swab sample from a subadult Egyptian rousette female bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus) in Matlapisi Cave, Limpopo Province, South Africa, 2017 (black filled circle; GenBank accession no. MT321489), and reference viruses, including the SPU191-13 bat 2764 Mahlapitsi strain (white circle; GenBank accession no. MG725616), detected in the same cave in July 2013. Complete and near-complete genome sequences from GenBank (accession numbers indicated) were aligned with the partial MARV sequence obtained from RSA-8095bat using MUSCLE version 3.8.31 (https://www.drive5.com/muscle), and RAxML version 8.2.10 (https://cme.h-its.org/exelixis/web/software/raxml/index.html) was used to infer the best-scoring maximum-likelihood tree after 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Node values indicate the bootstrap support values. Genomes isolated from bats are shown using a bat symbol. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. MARV, Marburg virus; RAVV, Ravn virus.