Volume 26, Number 2—February 2020
Research
Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection and Transmission in Poultry, United States1
Figure 5
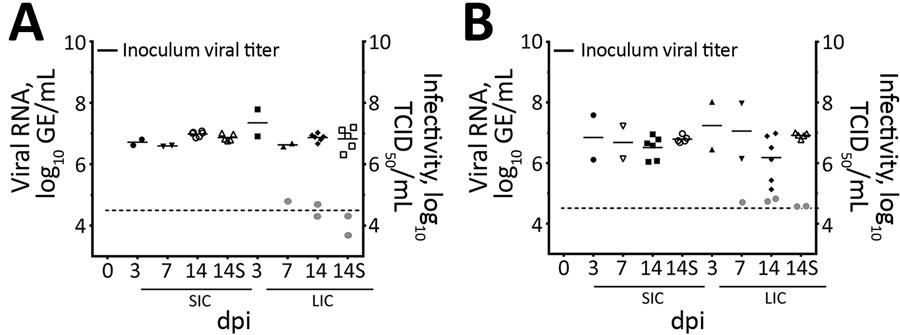
Figure 5. Viral RNA titers and infectivity of intestinal contents of (A) chicks and (B) poults in a study of infection and transmission of porcine deltacoronavirus in poultry. Inoculum viral titer represents the genomic equivalent (GE) of inoculum administered at onset, 9.71 log10 GE/mL. Gray dots represent infectivity at 7 and 14 dpi, expressed in log10 TCID50/mL, as indicated on the right y-axis. Dashed line indicates detection limit of 4.6 log10 GE/mL of PDCoV in samples. Shapes represent individual birds necropsied at each time point. Solid bars represent the mean. dpi, days postinoculation; GE, genomic equivalent; LIC, large intestine contents; S, sentinel birds necropsied; SIC, small intestine contents; TCID50, 50% tissue culture infectious dose.
1Preliminary results of this study were presented at the Conference of Research Workers in Animal Diseases, December 1–4, 2018, Chicago, Illinois, USA.