Volume 26, Number 3—March 2020
Research
Whole-Genome Sequencing to Detect Numerous Campylobacter jejuni Outbreaks and Match Patient Isolates to Sources, Denmark, 2015–2017
Figure 1
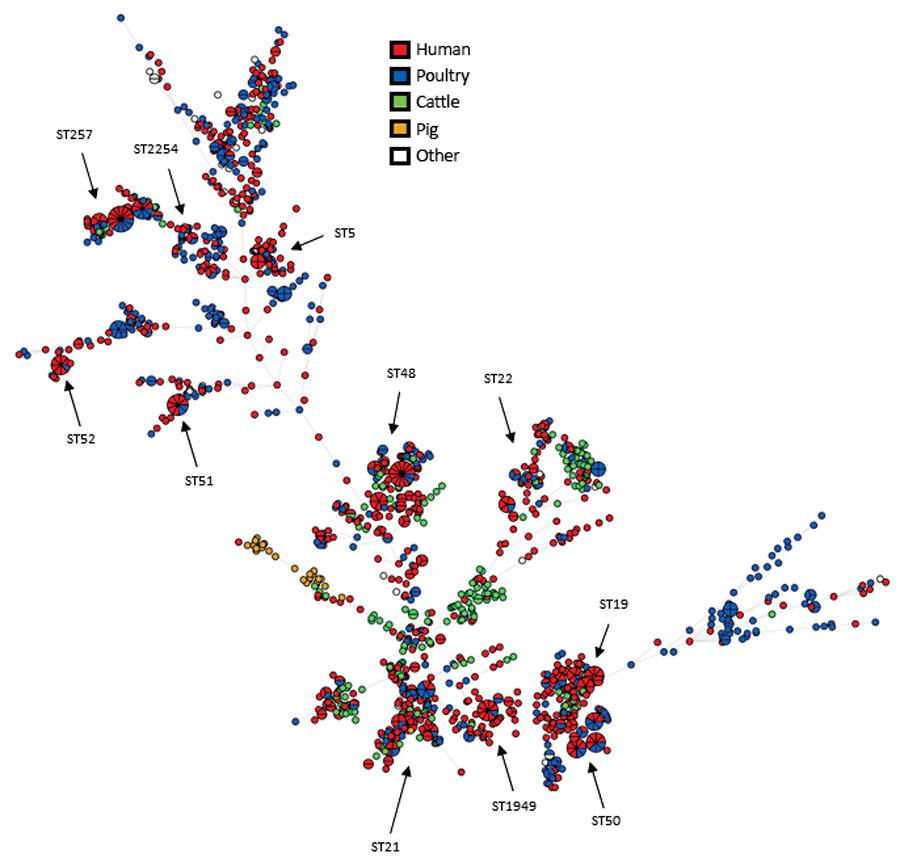
Figure 1. Overall phylogeny of 1,509 Camplylobacter jejuni isolates from Denmark, 2015–2017. Minimum spanning tree was based on core-genome multilocus sequence typing data. Colors indicate specific origin. Each small circle represents single isolates, and pie chart graphics represent multiple isolates with 0 allelic differences. Branch lengths represent the genetic (allelic) distances. The dataset displayed high diversity, and many genetic clusters were detected, in total 104 clusters of clinical isolates (n = 366). Forty-one of these clusters matched food/animal isolates; 34 matches to food/animal isolates were detected for sporadic clinical cases.
Page created: February 20, 2020
Page updated: February 20, 2020
Page reviewed: February 20, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.