Volume 26, Number 5—May 2020
Synopsis
Biphasic Outbreak of Invasive Group A Streptococcus Disease in Eldercare Facility, New Zealand
Figure
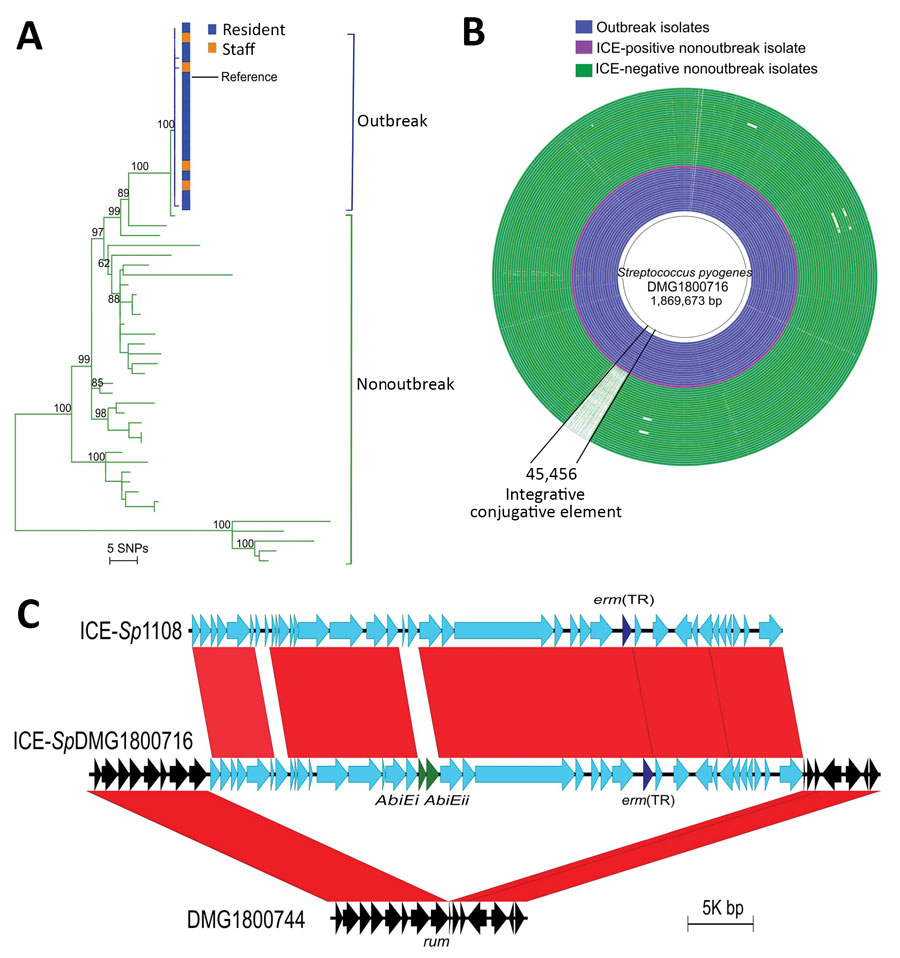
Figure. Comparative genomic analyses of 55 (18 outbreak and 37 nonoutbreak) associated emm81 group A Streptococcus (GAS) isolates from New Zealand, 2014. A) Midpoint-rooted maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analysis of the emm81 GAS population based on alignment of 336 high-quality single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Green branches indicate nonoutbreak isolates and blue branches indicate the clonal outbreak isolates. Outbreak isolates obtained from eldercare residents (blue) and staff members (orange) were indistinguishable at the whole-genome level. Numbers on major internal nodes indicate branch support as a percentage over 100 bootstrap replicates. The tree was created by using RAxML (13) and annotated by using iTOL (16). B) Comparative analyses of 55 emm81 draft genome assemblies from outbreak (blue) and nonoutbreak (green) isolates mapped against a new reference GAS genome from the outbreak, DMG1800716. A large DNA sequence coinciding with a 45.4-kb ICE, ICE-SpDMG1800716, is absent in the nonoutbreak isolates compared with all outbreak isolates. The image was created by using BLAST Ring Image Generator (12). C) Schematic representation and pairwise sequence comparison (BLASTn, https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) of ICE-SpDMG1800716 relative to the closest known homologue, ICE-Sp1108 (17). The genomic integration site of ICE-SpDMG1800716 is shown relative to a nonoutbreak emm81 isolate, DMG1800744. Red bars refer to 100% BLASTn homology as determined by Easyfig (18). The macrolide resistance gene erm(TR) is shown in dark blue and the abortive infection genes (AbiE) in green. ICE, integrative conjugative element; SNPs, single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
References
- Walker MJ, Barnett TC, McArthur JD, Cole JN, Gillen CM, Henningham A, et al. Disease manifestations and pathogenic mechanisms of Group A Streptococcus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014;27:264–301. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nelson GE, Pondo T, Toews K-A, Farley MM, Lindegren ML, Lynfield R, et al. Epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infections in the United States, 2005–2012. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:478–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williamson DA, Morgan J, Hope V, Fraser JD, Moreland NJ, Proft T, et al. Increasing incidence of invasive group A streptococcus disease in New Zealand, 2002-2012: a national population-based study. J Infect. 2015;70:127–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thigpen MC, Richards CL Jr, Lynfield R, Barrett NL, Harrison LH, Arnold KE, et al.; Active Bacterial Core surveillance / Emerging Infections Program Network. Invasive group A streptococcal infection in older adults in long-term care facilities and the community, United States, 1998-2003. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1852–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jordan HT, Richards CL Jr, Burton DC, Thigpen MC, Van Beneden CA. Group a streptococcal disease in long-term care facilities: descriptive epidemiology and potential control measures. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:742–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davies MR, Holden MT, Coupland P, Chen JH, Venturini C, Barnett TC, et al. Emergence of scarlet fever Streptococcus pyogenes emm12 clones in Hong Kong is associated with toxin acquisition and multidrug resistance. Nat Genet. 2015;47:84–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Beall B, Facklam R, Thompson T. Sequencing emm-specific PCR products for routine and accurate typing of group A streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:953–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chalker VJ, Smith A, Al-Shahib A, Botchway S, Macdonald E, Daniel R, et al. Integration of genomic and other epidemiologic data to investigate and control a cross-institutional outbreak of Streptococcus pyogenes. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:973–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nanduri SA, Metcalf BJ, Arwady MA, Edens C, Lavin MA, Morgan J, et al. Prolonged and large outbreak of invasive group A Streptococcus disease within a nursing home: repeated intrafacility transmission of a single strain. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25:248.e1–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Seemann T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:2068–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19:455–77. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alikhan N-F, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Beatson SA. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:402. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:1312–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu C-H, Xie D, et al. BEAST 2: a software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLOS Comput Biol. 2014;10:
e1003537 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Rambaut A, Lam TT, Max Carvalho L, Pybus OG. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016;2:
vew007 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):
W242-5 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Brenciani A, Tiberi E, Bacciaglia A, Petrelli D, Varaldo PE, Giovanetti E. Two distinct genetic elements are responsible for erm(TR)-mediated erythromycin resistance in tetracycline-susceptible and tetracycline-resistant strains of Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:2106–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA. Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:1009–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dale JB, Penfound TA, Chiang EY, Walton WJ. New 30-valent M protein-based vaccine evokes cross-opsonic antibodies against non-vaccine serotypes of group A streptococci. Vaccine. 2011;29:8175–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cornick JE, Kiran AM, Vivancos R, Van Aartsen J, Clarke J, Bevan E, et al. Epidemiological and molecular characterization of an invasive group A Streptococcus emm32.2 outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 2017;55:1837–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Galloway-Peña J, Clement ME, Sharma Kuinkel BK, Ruffin F, Flores AR, Levinson H, et al. Application of whole-genome sequencing to an unusual outbreak of invasive group A streptococcal disease. [-ofw.]. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3:
ofw042 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Williamson DA, Roos R, Verrall A, Smith A, Thomas MG. Trends, demographics and disparities in outpatient antibiotic consumption in New Zealand: a national study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71:3593–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dy RL, Przybilski R, Semeijn K, Salmond GPC, Fineran PC. A widespread bacteriophage abortive infection system functions through a Type IV toxin-antitoxin mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:4590–605. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mearkle R, Saavedra-Campos M, Lamagni T, Usdin M, Coelho J, Chalker V, et al. Household transmission of invasive group A Streptococcus infections in England: a population-based study, 2009, 2011 to 2013. Euro Surveill. 2017;22:30532. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adebanjo T, Apostol M, Alden N, Petit S, Tunali A, Torres S, et al. Evaluating household transmission of invasive group A Streptococcus disease in the United States using population-based surveillance data, 2013–2016. Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Aug 13;(ciz716). Epub ahead of print.
- Ahmed SS, Diebold KE, Brandvold JM, Ewaidah SS, Black S, Ogundimu A, et al. The role of wound care in 2 group A streptococcal outbreaks in a Chicago skilled nursing facility, 2015‒2016. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018;5:
ofy145 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.