Volume 26, Number 5—May 2020
Research Letter
Diplorickettsia Bacteria in an Ixodes scapularis Tick, Vermont, USA
Figure
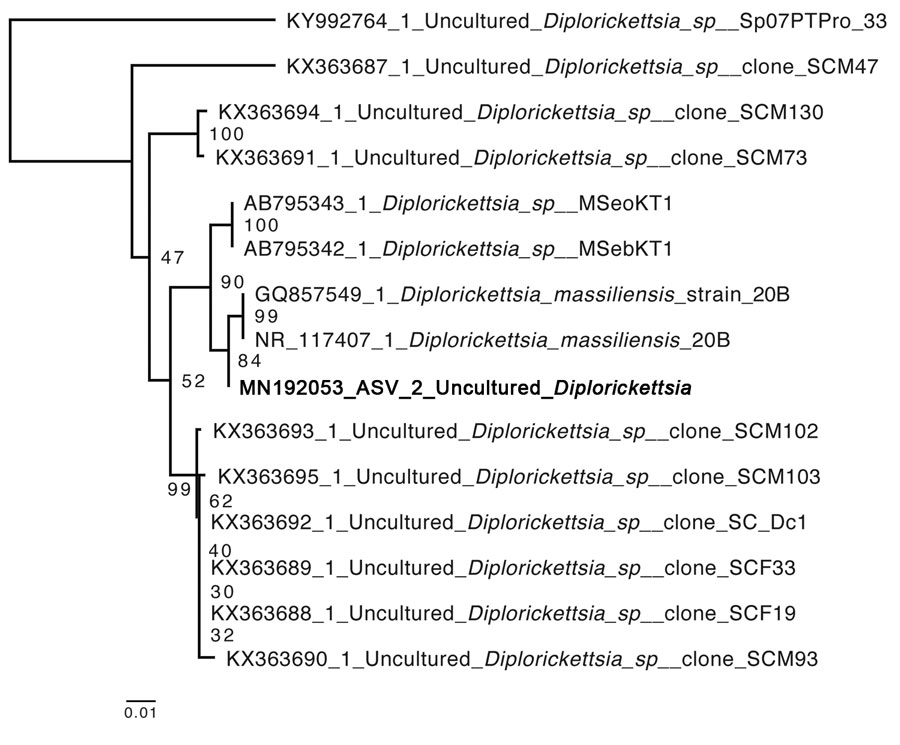
Figure. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of a MAFFT alignment (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server) of the V3–V4 region of the Diplorickettsia 16S rRNA gene, including the novel amplicon sequence variant identified in Vermont, USA (bold). A total of 427 bases were aligned and 363 conserved sites were used for neighbor-joining phylogeny, with 100 bootstrap iterations. The 341F and 875R primers were used to amplify these regions (6). Default alignment parameters were used for alignment and generation of phylogenetic tree. Numbers at nodes indicate bootstrap values after 1,000 bootstrapping iterations. GenBank accession numbers are indicated. Scale bar represents average number of substitutions per site.
References
- Buller RS, Arens M, Hmiel SP, Paddock CD, Sumner JW, Rikhisa Y, et al. Ehrlichia ewingii, a newly recognized agent of human ehrlichiosis. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:148–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dumler JS, Choi K-S, Garcia-Garcia JC, Barat NS, Scorpio DG, Garyu JW, et al. Human granulocytic anaplasmosis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1828–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Telford SR III, Goethert HK, Molloy PJ, Berardi VP, Chowdri HR, Gugliotta JL, et al. Borrelia miyamotoi disease: neither Lyme disease nor relapsing fever. Clin Lab Med. 2015;35:867–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Feder HM Jr, Johnson BJB, O’Connell S, Shapiro ED, Steere AC, Wormser GP; Ad Hoc International Lyme Disease Group. A critical appraisal of “chronic Lyme disease”. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1422–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Van Treuren W, Ponnusamy L, Brinkerhoff RJ, Gonzalez A, Parobek CM, Juliano JJ, et al. Variation in the microbiota of Ixodes ticks with regard to geography, species, and sex. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015;81:6200–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T, Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M, et al. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:
e1 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods. 2016;13:581–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mediannikov O, Sekeyová Z, Birg M-L, Raoult D. A novel obligate intracellular gamma-proteobacterium associated with ixodid ticks, Diplorickettsia massiliensis, Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov. PLoS One. 2010;5:
e11478 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Subramanian G, Mediannikov O, Angelakis E, Socolovschi C, Kaplanski G, Martzolff L, et al. Diplorickettsia massiliensis as a human pathogen. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;31:365–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: April 06, 2020
Page updated: April 06, 2020
Page reviewed: April 06, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.