Volume 26, Number 7—July 2020
Synopsis
Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections in Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Figure 5
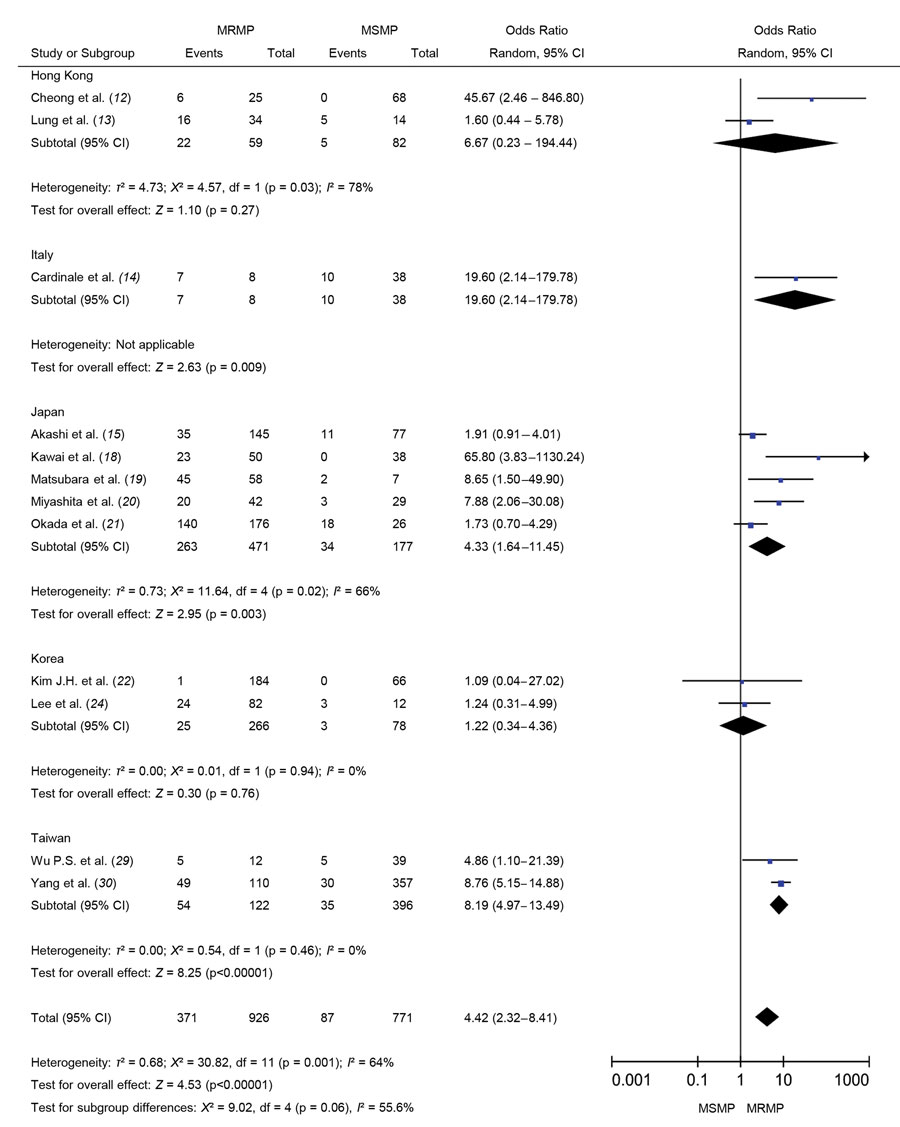
Figure 5. Forest plots comparing MRMP and MSMP by the pooled odds ratio of changing antibiotics in meta-analysis of MRMP infections in pediatric community-acquired pneumonia. MRMP, macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae; MSMP, macrolide-sensitive Mycoplasma pneumoniae; OR, odds ratio.
1All authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: April 03, 2020
Page updated: June 18, 2020
Page reviewed: June 18, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.