Volume 26, Number 7—July 2020
Dispatch
Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 by WHO-Recommended Hand Rub Formulations and Alcohols
Figure 2
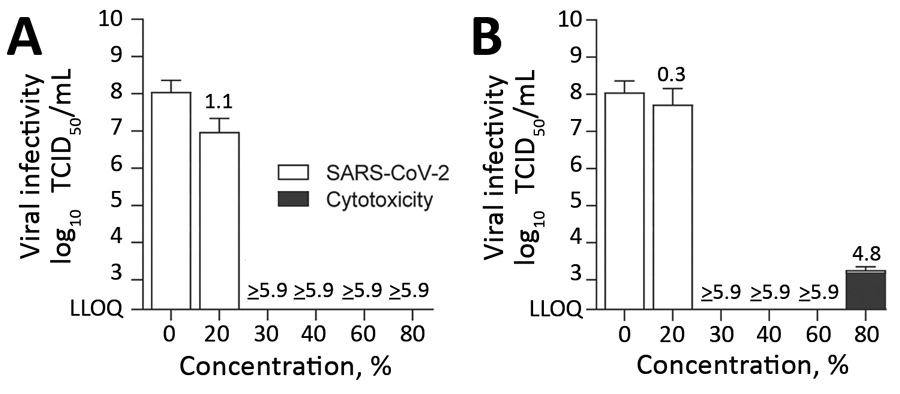
Figure 2. Effect of commercially available alcohols in inactivating SARS-CoV-2. The means of 3 independent experiments with SDs (error bars) are shown. A) Results for ethanol. B) Results for 2-propanol. Dark gray bar indicates cytotoxic effects, calculated analogous to virus infectivity. Reduction factors are included above the bar. The biocide concentrations ranged from 0–80% with an exposure time of 30 s. Viral titers are displayed as TCID50/mL values. LLOQ, lower limit of quantification; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TCID50/mL, 50% tissue culture infectious dose.
Page created: April 13, 2020
Page updated: June 18, 2020
Page reviewed: June 18, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.