Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Research Letter
mcr-Positive Escherichia coli ST131-H22 from Poultry in Brazil
Figure
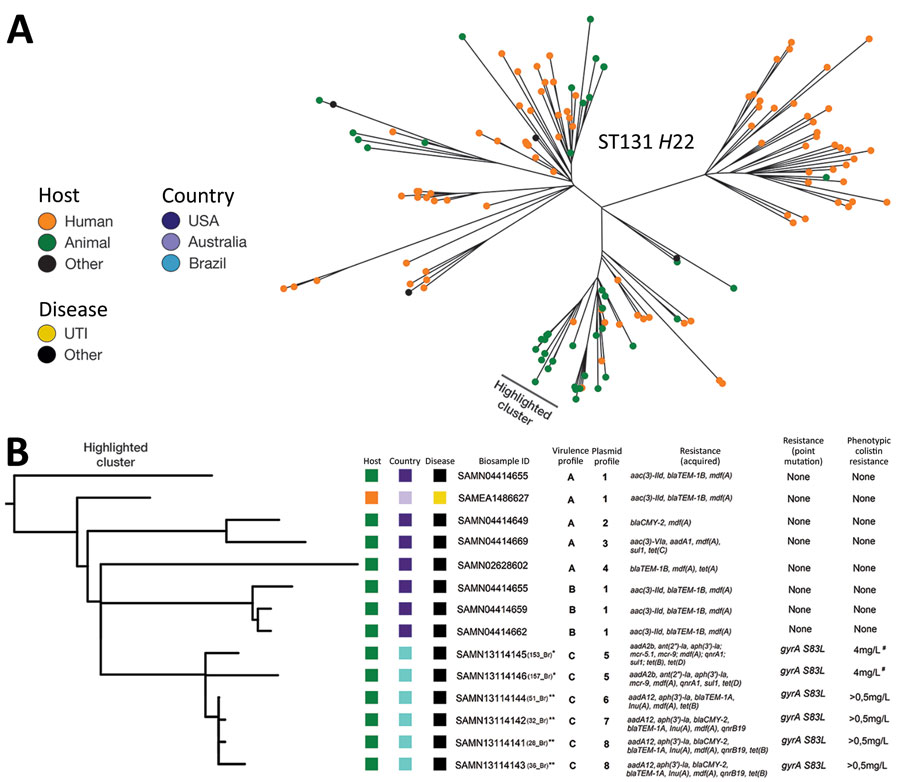
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of Escherichia coli ST131-H22 isolates from poultry in Brazil and reference sequences. A) Unrooted phylogeny of 146 E. coli ST131-H22 isolates based on core genome single-nucleotide polymorphisms with the host origin outlined. The cluster containing closely related isolates to the 6 isolates from Brazil is highlighted. B) Rooted phylogeny of closely related isolates from retail meat with APEC and a human isolate with our 6 APEC isolates. The highlighted cluster includes a partial depiction of the tree including the data on host, country, and disease (urinary tract infection or other). Clusters containing the study’s isolates have their individual identification in parenthesis. Asterisks indicate farm origins (*, farm 1; **, farm 2). Virulence factors profiles are identified as groups A: cvi/cva, ent, fimA-H, ibeA, irp1/2, iroN, iucD,iss, kpsM, ompA, tsh; B: cvi/cva, ent, fimA-H, ibeA, irp1/2, iroN, iucD, iss, kpsM, ompA; and C: cvi/cva, ent, fimA-H, fyuA, ibeA, irp1/2, iroN, iucD, iss, kpsM, ompA, tsh. Plasmid profiles are identified by group: 1: IncFIB, IncFIC(FII), Incl1; 2: IncFIB, IncFIC(FII), IncFII, Incl1; 3: IncFIB, IncFIC(FII), IncFII, IncHI2, IncHI2A, Incl1; 4: IncFIB, IncFIC(FII), Incl1, IncN; 5: IncFIB, IncFIC(FII), IncFII, IncFII(pCoo), IncHI2, IncHI2A; 6: IncFIB, IncFIC(FII), IncFII, IncHI2, IncHI2A; 7: IncFIB, IncFII, Incl1, IncX1; and 8: IncFIB, IncFIC(FII), IncFII, Incl1, IncX1. Phenotypic colistin-resistance is indicated by the symbol # for the 2 colistin-resistance mcr genes positive isolates, showing resistance according to 2018 Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (https://clsi.org/) clinical breakpoints. APEC, avian pathogenic E. coli; ID, identification; ST, sequence type; UTI, urinary tract infection.