Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Dispatch
Sequence Type Changes Associated with Decreasing Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Japan
Figure 1
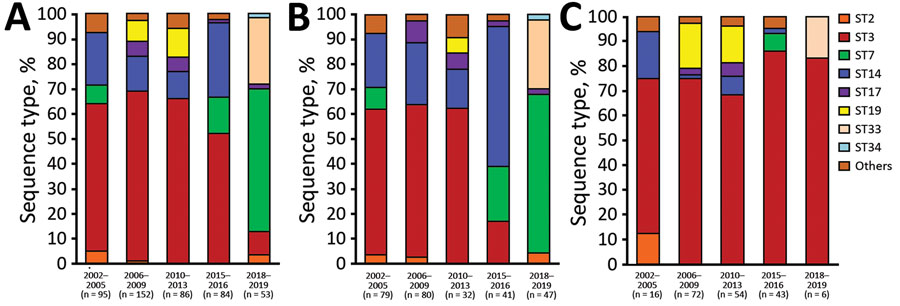
Figure 1. Relationships between year of isolation and STs among 279 macrolide-susceptible M. pneumoniae and 191 macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae from children in Japan, 2002–2019. A) All strains tested; B) macrolide-susceptible strains; C) macrolide-resistant strains. Others includes ST13 (2005), ST15 (2002, 2016), ST16 (2002, 2010), ST18 (2010), ST20 (2004), ST21 (2011), ST 22 (2003, 2006, 2016), ST29 (2016), and ST30 (2016). ST, sequence type.
Page created: June 09, 2020
Page updated: August 19, 2020
Page reviewed: August 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.