Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Synopsis
Encephalopathy and Encephalitis Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytokine Alterations and Coronavirus Disease, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 2020
Figure 2
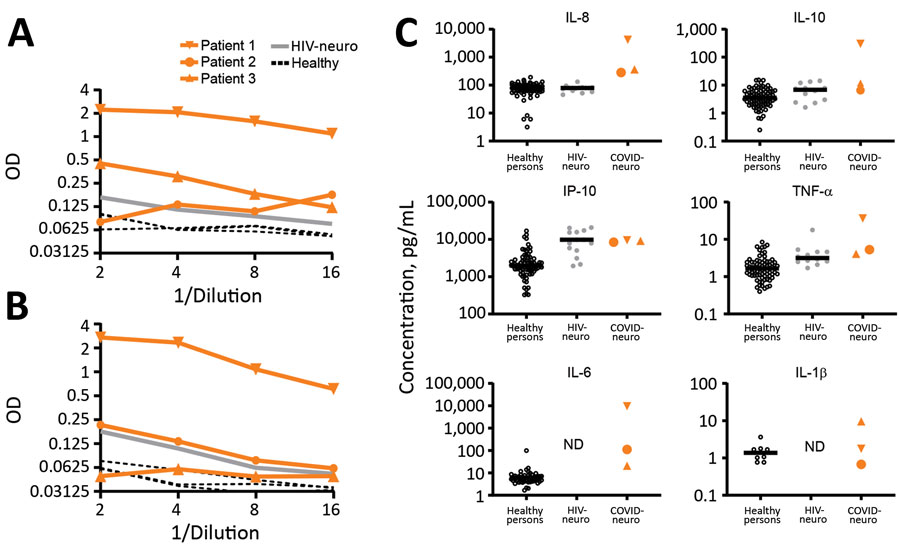
Figure 2. Cerebrospinal fluid (A and B) and inflammatory protein (C) analyses for patients with coronavirus disease and neurologic complications, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 2020. Compared with healthy controls and patients who had HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder, CSF levels of anti-S1 IgM were high in patient 1, and moderately high in patients 2 and 3. In contrast, levels of CSF anti-E IgM were high only for patient 1 and within references ranges for patients 2 and 3. CSF inflammatory analysis showed increased levels of IL-8 and IL-10 more unique to neuro-COVID, and increased levels of IP-10 and TNF-α in neuro-COVID and HIV-neuro. Circles indicate patients whose interleukin levels were tested and used as controls (healthy, HIV). Horizontal bars indicate average values. COVID-neuro, coronavirus disease–associated neurologic complications; HIV-neuro, HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder; IL, interleukin; IP, interferon-γ–induced protein; OD, optical density, ND, not determined; neuro-COVID, neurologic complications associated with coronavirus disease; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.