Volume 27, Number 11—November 2021
Dispatch
Epidemiologic Analysis of Efforts to Achieve and Sustain Malaria Elimination along the China–Myanmar Border
Figure 2
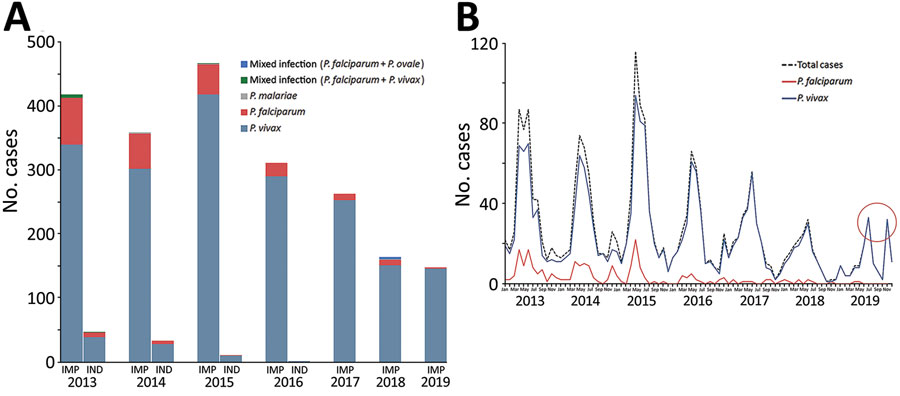
Figure 2. Malaria cases in the 18 counties in China along the border with Myanmar, 2013–2019. A) Proportions of Plasmodium species cases. B) Monthly reported malaria cases. Red circle highlights the double peaks identified in July and November 2019. IMP, imported; IND, indigenous.
Page created: August 25, 2021
Page updated: October 19, 2021
Page reviewed: October 19, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.