Volume 27, Number 2—February 2021
Research
Effects of Social Distancing Measures during the First Epidemic Wave of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Infection, Greece
Figure 2
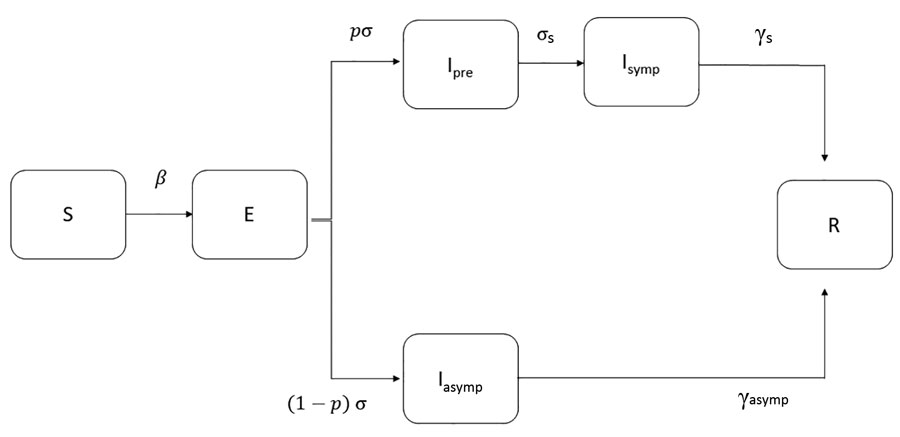
Figure 2. Modified susceptible-exposed-infectious-recovered (SEIR) model used to estimate the course of the first epidemic wave of coronavirus disease, Greece. Cases are classified into susceptible (S), exposed (E), infectious (I, which is divided into 3 conditions: Ipre, before developing symptoms, Isymp for clinically ill, or Iasymp for true asymptomatic), and recovered (R). We assumed that a proportion (p) of exposed cases will develop symptoms and that infectiousness can occur before the onset of symptoms. β is the rate at which persons become infected and move to E; exposed individuals become infectious at a rate σ and presymptomatic infectious cases develop symptoms at a rate σs; γasymp is the rate of recovery for asymptomatic persons; γs is the rate of recovery for symptomatic persons.
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.