Volume 27, Number 3—March 2021
Dispatch
Bedaquiline as Treatment for Disseminated Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infection in 2 Patients Co-Infected with HIV
Figure 1
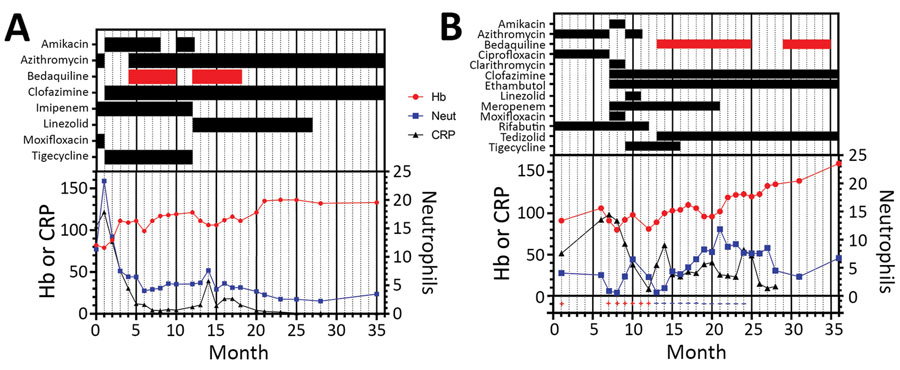
Figure 1. Summary of treatment and monitoring of 2 HIV-positive persons who had disseminated Mycobacterium abscessus infections, London, UK. A) Case-patient 1. B) Case-patient 2. The infection in case-patient 1 was secondary to fecal abdominal cavity contamination after rectal perforation. Bars in top section show timing of treatments; red indicates bedaquiline. Drug regimens and treatment responses were measured by using Hb (g/L), Neut (× 109 cells/L), and CRP (mg/L). Values (+ and –) on the bottom of panel B are results for mycobacterial blood cultures. CRP, C-reactive protein; Hb, hemoglobin; Neut, neutrophils.
Page created: November 11, 2020
Page updated: February 21, 2021
Page reviewed: February 21, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.