Volume 27, Number 3—March 2021
Research
Clusters of Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Detected by Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of Nationwide Sample, Thailand, 2014–2017
Figure 4
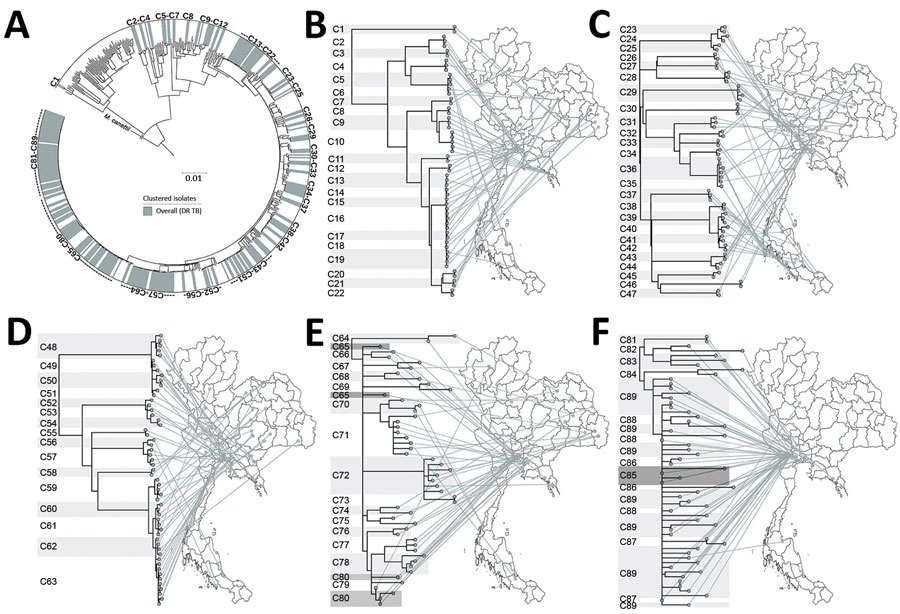
Figure 4. All clusters of DR TB isolates from Thailand. A) A total of 89 clusters are highlighted in the outer circle. Scale bar indicates the genetic distance proportional to the total number of single nucleotide polymorphisms. B–F) Phylogeographical links of each cluster are shown. For clarity, clusters are divided among 5 phylomaps. Some isolates in closely related clusters (C64–C65, C79–C80, and C85–C89) crossed localities. Mycobacterium canetti was used as an outgroup. DR TB, drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Page created: December 29, 2020
Page updated: February 21, 2021
Page reviewed: February 21, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.