Volume 27, Number 7—July 2021
Dispatch
Prevalence of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in Dromedary Camels, Tunisia
Figure 2
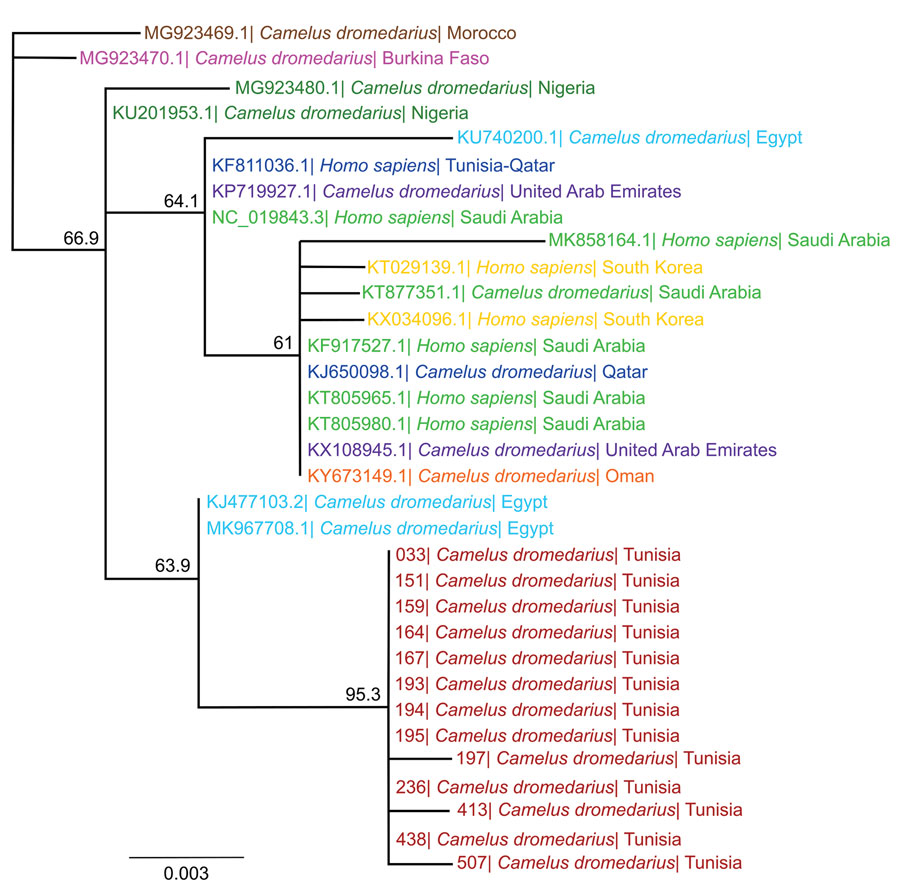
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of MERS-CoV samples from dromedary camels in Tunisia, conducted by using the spike RBD. We used 720-bp fragments of the MERS-CoV spike RBD amplified from nasal swab samples of 13 dromedary camels and published RBD sequences of representative MERS-CoV strains from other countries to create the phylogenetic tree using Geneious Prime Tree Builder (Geneious Biologics, https://www.geneious.com). Branches are shaded by country: red represents sequences from Tunisia (this study); brown represents Morocco, pink Burkina Faso, dark green Nigeria, blue Egypt, dark blue Qatar, green Saudi Arabia, yellow South Korea, purple United Arab Emirates, and orange Oman. GenBank accession numbers are provided for reference sequences. Numbers indicate bootstrap values (1,000 pseudo-replicates). Scale bar indicates sequence divergence (% nucleotide substitutions). MERS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; RBD, receptor-binding protein.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.