Volume 28, Supplement—December 2022
SUPPLEMENT ISSUE
Clinical
Effects of Decreased Immunization Coverage for Hepatitis B Virus Caused by COVID-19 in World Health Organization Western Pacific and African Regions, 2020
Figure 2
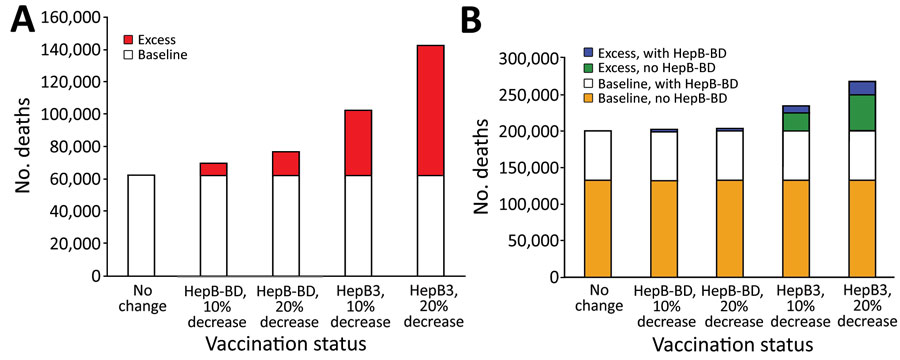
Figure 2. Numbers of additional hepatitis B virus (HBV)–related deaths after decreased coverage for hepatitis B vaccine caused by COVID-19 in World Health Organization (WHO) Western Pacific Region (WPR) and African Region (AFR), 2020. We used a mathematical model to estimate the effect of decreased hepatitis B vaccination coverage on HBV-related deaths among children born in 2020 compared with 2019. A) Total number of HBV-related deaths determined from 2019 data (baseline) and estimates of excess deaths after 10% or 20% decrease in birth dose (HepB-BD) or third-dose hepatitis B (HepB3) vaccination coverage in the WHO WPR. All countries and areas in the WPR have introduced HepB-BD, including 2 countries that provide HepB-BD only to infants born to hepatitis B surface antigen–positive mothers. B) Total number of HBV-related deaths (baseline) and estimates of excess deaths after 10% or 20% decrease in HepB-BD or HepB3 vaccination coverage in the WHO AFR. Comparisons were made between countries with and without HepB-BD. Fourteen countries in the AFR have introduced HepB-BD, including 1 country that provides HepB BD-only to infants born to hepatitis B surface antigen–positive mothers. HepB-BD coverage data were only available for countries providing universal birth doses. HepB-BD, birth dose; HepB3, third-dose hepatitis B.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.