Evaluation of Commercially Available High-Throughput SARS-CoV-2 Serologic Assays for Serosurveillance and Related Applications
Mars Stone
1
, Eduard Grebe
1, Hasan Sulaeman, Clara Di Germanio, Honey Dave, Kathleen Kelly, Brad J. Biggerstaff, Bridgit O. Crews, Nam Tran, Keith R. Jerome, Thomas N. Denny, Boris Hogema, Mark Destree, Jefferson M. Jones, Natalie Thornburg, Graham Simmons, Mel Krajden, Steve Kleinman, Larry J. Dumont, and Michael P. Busch
Author affiliations: Vitalant Research Institute, San Francisco, California, USA (M. Stone, E. Grebe, H. Sulaeman, C. Di Germanio, H. Dave, K. Kelly, G. Simmons, L.J. Dumont, M.P. Busch); University of California–San Francisco, San Francisco (M. Stone, E. Grebe, G. Simmons, M.P. Busch); South African Centre for Epidemiological Modelling and Analysis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa (E. Grebe); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA (B.J. Biggerstaff); University of California Irvine Medical Center, Orange, California, USA (B.O. Crews); University of California–Davis, Davis, California, USA (N. Tran); Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA (K.R. Jerome); Duke Human Vaccine Institute, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, USA (T.N. Denny); Sanquin Research, Amsterdam, the Netherlands (B. Hogema); BloodWorks NorthWest, Seattle (M. Destree); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (J.M. Jones, N. Thornburg); British Columbia Centre for Disease Control, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada (M. Krajden); University of British Columbia, Vancouver (S. Kleinman); University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, Colorado, USA (L.J. Dumont)
Main Article
Figure 3
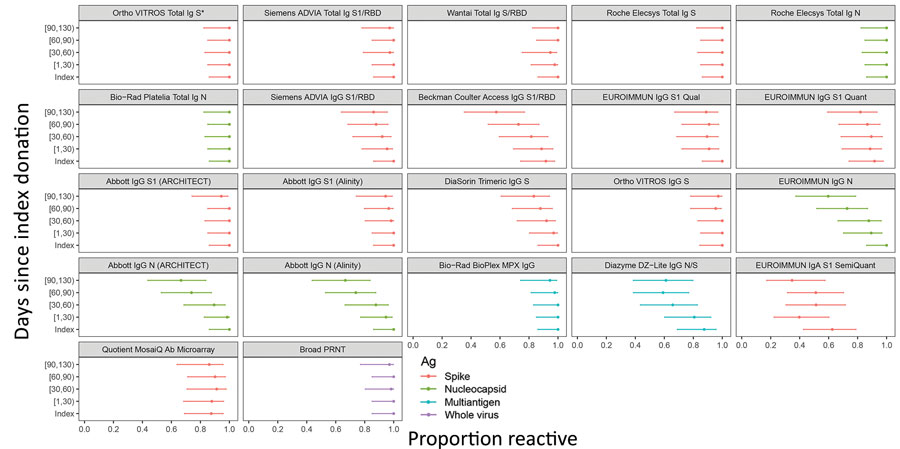
Figure 3. Proportion of donors with detectable severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 antibodies in study of commercially available high-throughput assays for serosurveillance. In the longitudinal coronavirus disease convalescent plasma donor cohort, donations were sorted into time bins relative to index donation. Time bin labels on x-axis are denoted with brackets to indicate inclusive boundaries and parentheses to indicate exclusive boundaries. Donors who contributed >1 donation in a time bin contributed the fractional proportion reactive to the numerator and 1 to the denominator for estimation of proportion reactive in the time bin. Symbols indicate point estimates of proportion reactive, and bars indicate 95% CIs (Wilson score). Assays are described in Table 1. Each of the 24 donors had an index sample available. For time bins 1–29 days post index, n = 22 donors, n = 56 specimens; day 30–59, n = 19 donors, n = 45 specimens; day 60–89, n = 22 donors, n = 54 specimens; day 90+, n = 18 donors, n = 30 specimens. Ortho VITROS Total Ig anti-S reactivity was required for qualification of continued CCP donation and therefore shows 100% detection in all time bins by definition. Ab, antibody; Ag, antigen; N, nucleocapsid; PRNT, plaque reduction neutralization test; RBD, receptor binding domain; S, spike protein.
Main Article
Page created: January 12, 2022
Page updated: February 21, 2022
Page reviewed: February 21, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
