Volume 28, Number 3—March 2022
Research
Retrospective Cohort Study of Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Notifications, Vietnam, 2020
Figure 3
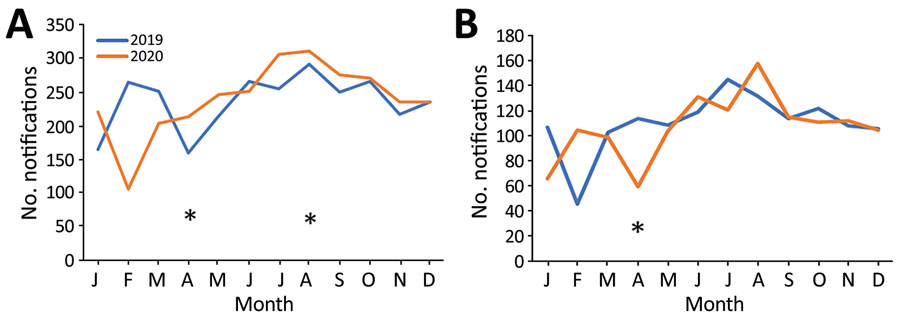
Figure 3. Change in number of monthly notifications for multidrug-resistant/rifampin-resistant tuberculosis during the COVID-19 pandemic, Vietnam, 2019–2020. A) Vietnam; B) Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. Asterisks indicate timing of COVID-19 outbreaks. COVID-19, coronavirus disease.
Page created: February 04, 2022
Page updated: February 21, 2022
Page reviewed: February 21, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.