Volume 28, Number 4—April 2022
Synopsis
Phylogenetic Analysis of Spread of Hepatitis C Virus Identified during HIV Outbreak Investigation, Unnao, India
Figure 1
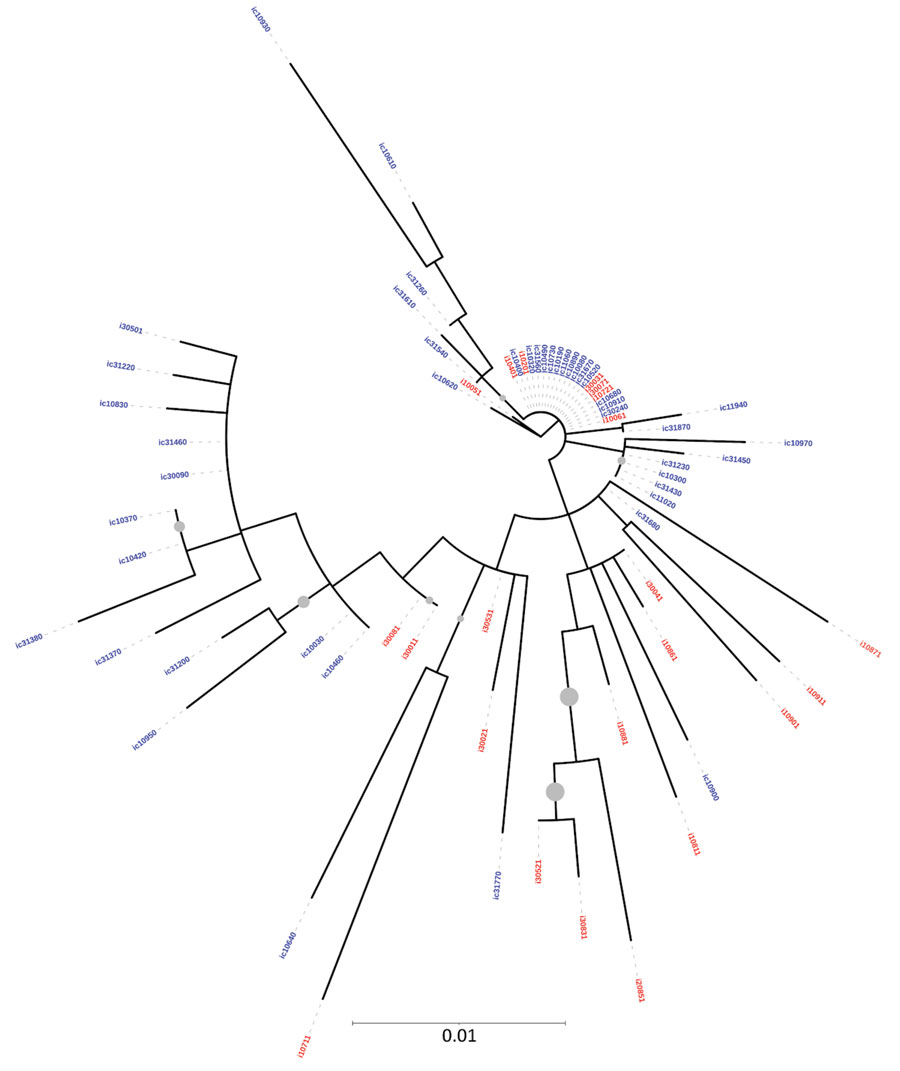
Figure 1. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree derived using hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B gene sequences of isolates from anti-HCV positive persons identified during HIV outbreak investigation, Unnao, India. Grey circles indicate nodes with >70% bootstrap support. Red indicates samples with HIV–HCV co-infection; blue indicates samples with HCV monoinfection. i, HIV–HCV co-infection; ic, HCV monoinfection.
Page created: February 15, 2022
Page updated: March 21, 2022
Page reviewed: March 21, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.