Volume 28, Number 7—July 2022
Dispatch
Chronic Pulmonary Disease Caused by Tsukamurella toyonakaense
Figure 1
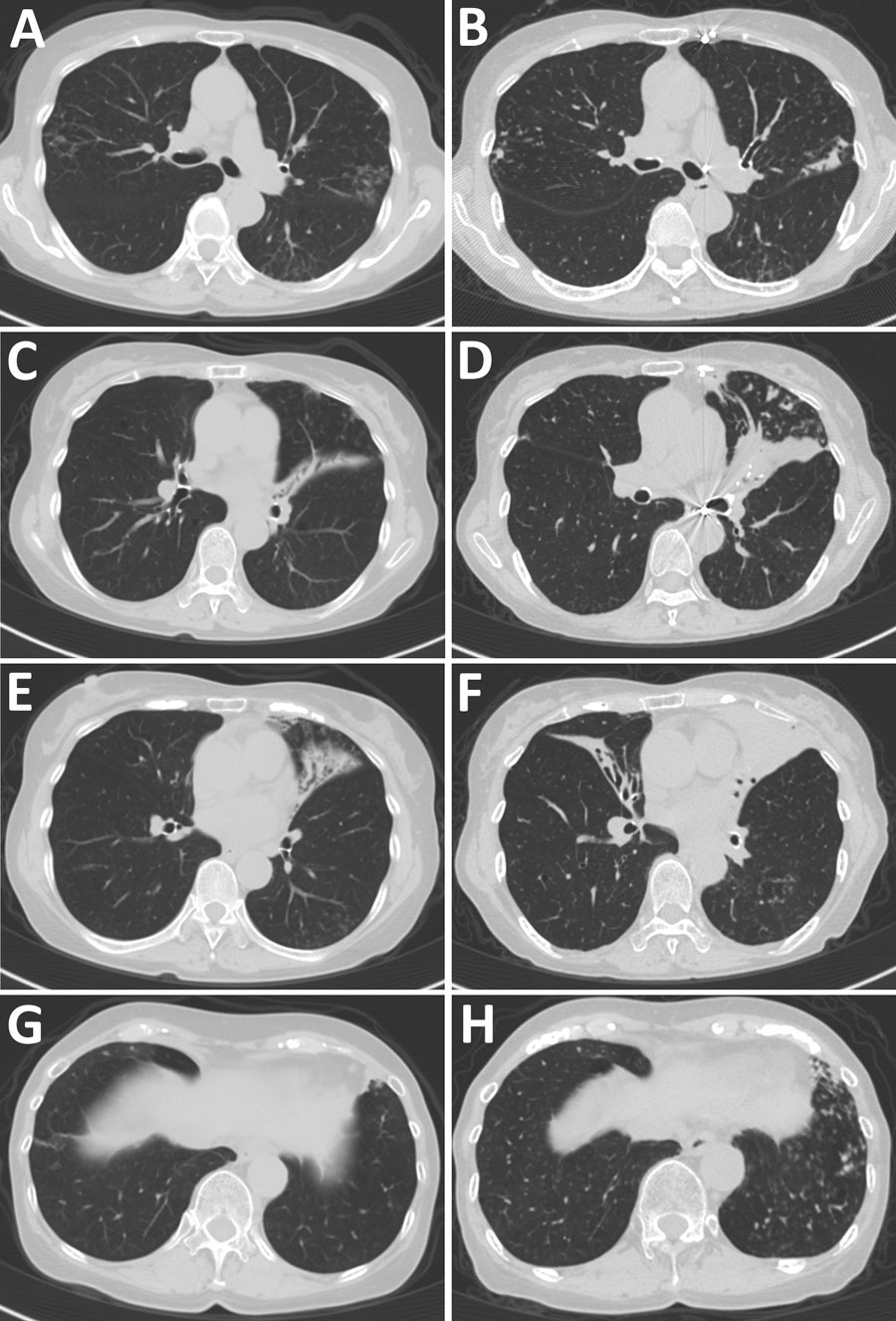
Figure 1. Comparison of chest computed tomography findings over time for patient who had chronic pulmonary disease caused by Tsukamurella toyonakaense. Findings are shown from before Tsukamurella species was detected (A, C, E, and G) and 6 years later (B, D, F, and H). A and B show that nodules in right segment 2 and left segment 6 were unchanged. C and D show that bronchiectasis in lingula had progressed. E and F show that bronchiectasis newly appeared in the middle lobe. G and H show that nodules newly appeared in left segments 8–10.
Page created: May 03, 2022
Page updated: June 18, 2022
Page reviewed: June 18, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.