Volume 28, Number 9—September 2022
Dispatch
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Incidence, South Korea, 2001–2019
Figure 2
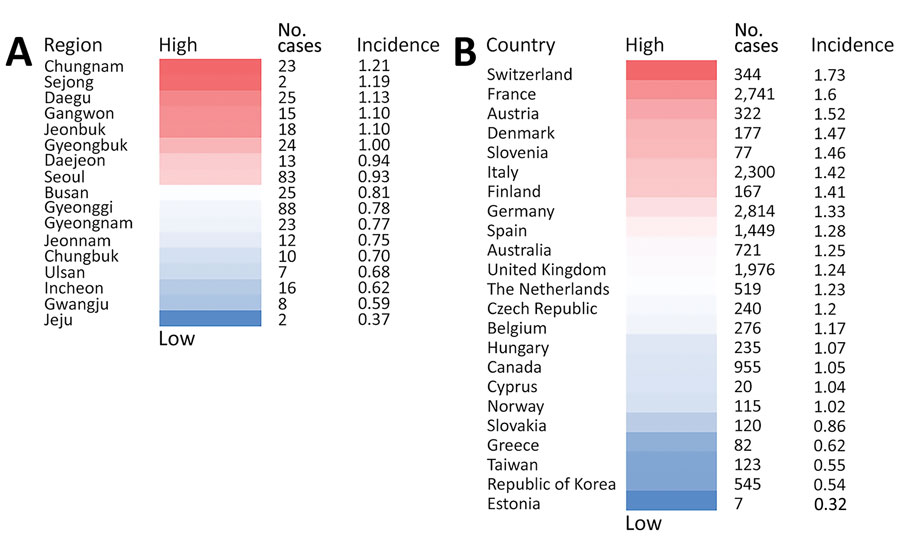
Figure 2. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) incidence, South Korea and globally, 2001–2019. A) Number of cases and incidence per million persons in cities and provinces of South Korea, including probable, possible, and definite CJD diagnoses. B) Global number of sporadic CJD cases and incidence per million population by country (4). Sporadic CJD incidence for South Korea is from this study.
References
- Kim YC, Won SY, Jeong BH. Altered expression of glymphatic system-related proteins in prion diseases: Implications for the role of the glymphatic system in prion diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:2281–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Uttley L, Carroll C, Wong R, Hilton DA, Stevenson M. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a systematic review of global incidence, prevalence, infectivity, and incubation. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:e2–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Asante EA, Linehan JM, Desbruslais M, Joiner S, Gowland I, Wood AL, et al. BSE prions propagate as either variant CJD-like or sporadic CJD-like prion strains in transgenic mice expressing human prion protein. EMBO J. 2002;21:6358–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Collinge J, Palmer MS, Dryden AJ. Genetic predisposition to iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1991;337:1441–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kovács GG, Puopolo M, Ladogana A, Pocchiari M, Budka H, van Duijn C, et al.; EUROCJD. Genetic prion disease: the EUROCJD experience. Hum Genet. 2005;118:166–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jeong BH, Kim YS. Genetic studies in human prion diseases. J Korean Med Sci. 2014;29:623–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. WHO infection control guidelines for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Geneva: The Organization; 2000.
- Chandra S, Mahadevan A, Shankar SK. Familial CJD—brief commentary. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2019;22:462–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Arata H, Takashima H. [Familial prion disease (GSS, familial CJD, FFI)]. Nihon Rinsho. 2007;65:1433–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: July 31, 2022
Page updated: August 19, 2022
Page reviewed: August 19, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.