Volume 29, Number 1—January 2023
Dispatch
Successful Treatment of Balamuthia mandrillaris Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis with Nitroxoline
Figure 2
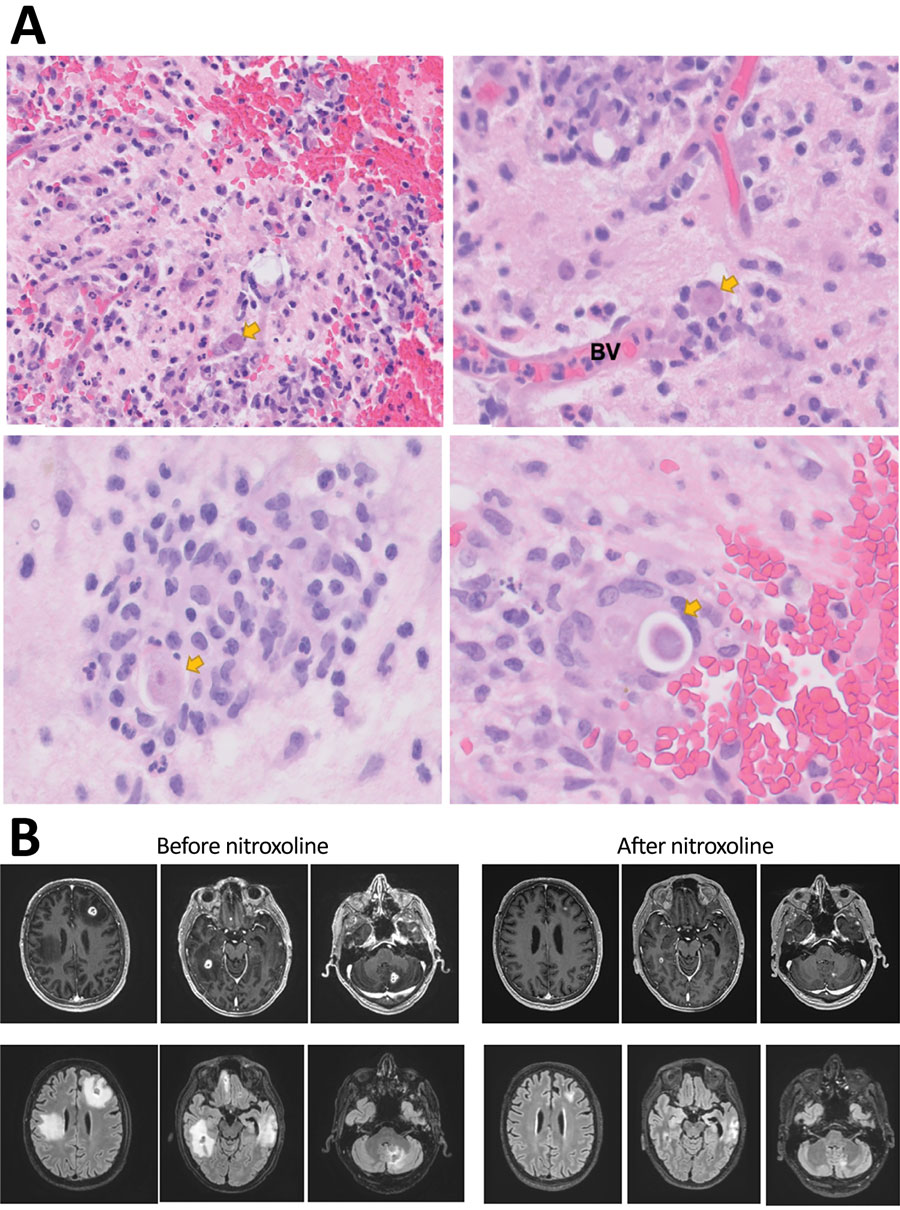
Figure 2. Diagnostic findings for patient with granulomatous amebic encephalitis, California, USA. A) Brain biopsy sample. Granulomas are noted in a perivascular pattern. Scattered structures (arrows) with large nuclei and abundant cytoplasma are concerning for amebic trophozoite forms. Occasional structures with a large nucleus present within a relatively rigid outline (lower right image) are suspicious for amebic cysts, the dormant, thick-walled life stage. B) Magnetic resonance images obtained before and after nitroxoline treatment. Upper row shows axial gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted images; lower row shows axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images. Images in the left series were obtained on day 96 after initial visit, 1 week before nitroxoline initiation; images in the right series were obtained on day 156 after initial visit, 7 weeks after nitroxoline initiation. BV, blood vessel.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.