Volume 29, Number 11—November 2023
Research
Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Deaths Attributable to Antimicrobial Resistance, Latin America
Figure 3
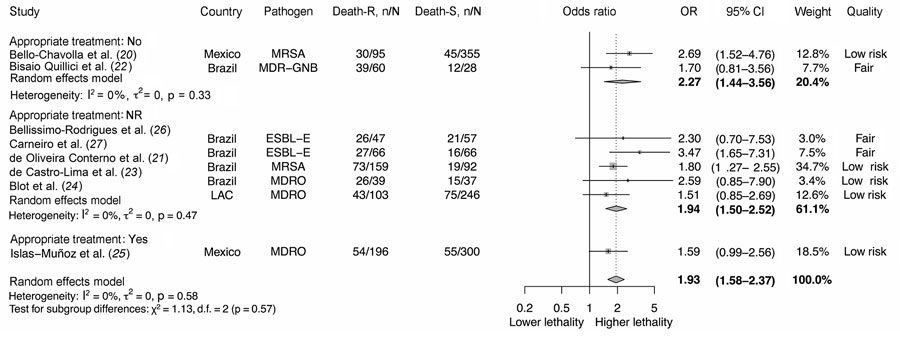
Figure 3. Adjusted odds ratios between antimicrobial resistance and lethality by appropriate empirical antibiotic treatment (considering the definition of appropriate empirical treatment given by each author) in systematic review and meta-analysis of deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance, Latin America. Death-R indicates death in the resistant group; Death-S indicates death in the susceptible group. Error bars indicate 95% CIs. CR-AB, carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii; CRE, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales; CR-PA, carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; ESBL-E, extended-spectrum β-lactamase–producing Enterobacterales; MDR-GNB, multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli (including ESBL-E, CRE, CR-PA, CR-AB); MDRO, multidrug-resistant organisms (including MRSA, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, ESLB-E, CRE, CR-PA, CR-AB); MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; NR, not reported; OR, odds ratio.