Volume 29, Number 12—December 2023
Research Letter
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) from Wild Birds, Poultry, and Mammals, Peru
Figure
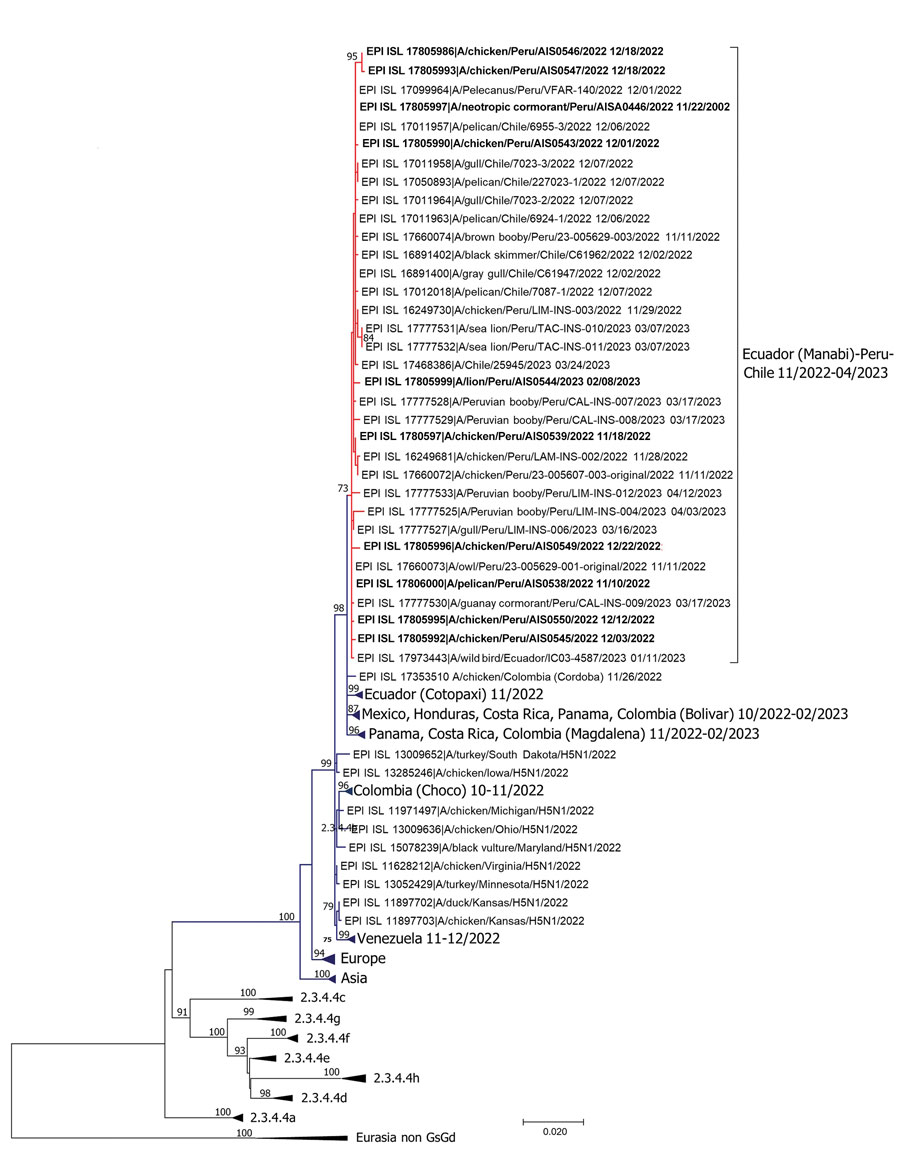
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) from wild birds, poultry, and mammals, Peru. Maximum-likelihood method was used for phylogeny of 101 hemagglutinin H5 sequences from avian influenza viruses. Red lines indicate clustering of strains from Peru and sequences from this study; bold font indicates the sequences from this study. Dark blue lines indicate other strains from South and North America. Non–goose/Guangdong lineage virus strains from Eurasia were outgroups. Phylogenetic tree was generated and edited with MEGA X software (https://www.megasoftware.net). Sequences were aligned by using the MUSCLE program in the AliView alignment viewer and editor (https://www.ormbunkar.se/aliview). We used general time reversible and gamma distribution models; robustness of tree topology was assessed with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Only bootstrap values >70% are shown. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.