Volume 29, Number 3—March 2023
Synopsis
Yellow Fever Vaccine–Associated Viscerotropic Disease among Siblings, São Paulo State, Brazil
Figure 2
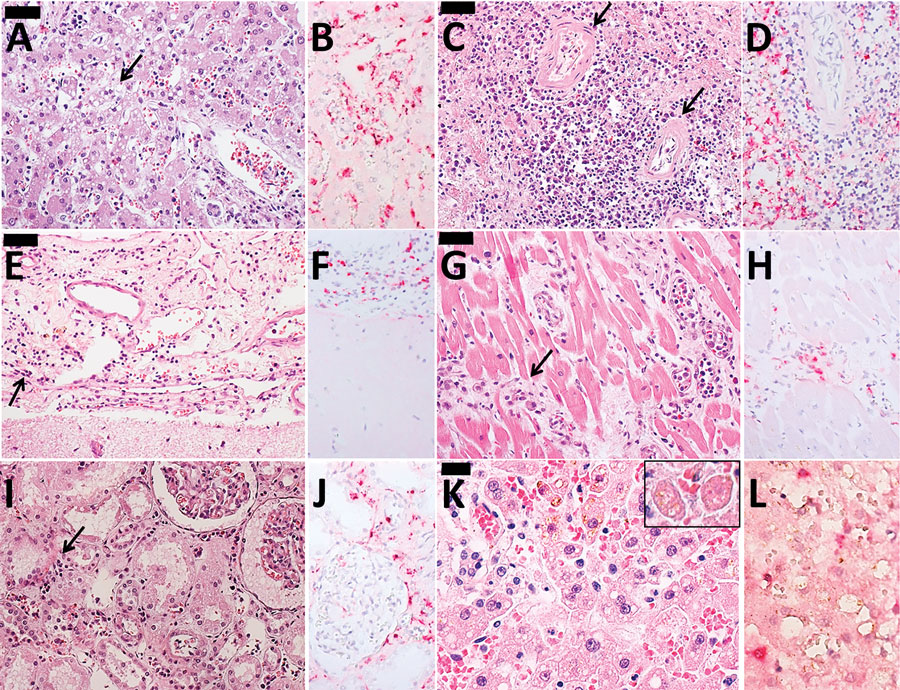
Figure 2. Histopathological findings in 2 case-patients with fatal reaction to 17DD yellow fever (YF) vaccine, São Paolo state, Brazil, 2017–2018. A, B) Liver tissue from case 1: A) steatotic hepatitis (arrow) with scarce inflammatory reaction and rare apoptotic bodies; B) immunostaining for YF antigens in Kuppfer cells and inflammatory cells in the portal tract. C, D) Spleen tissue from case 1: C) lymphoid hypoplasia (arrows); D) YF antigens in cells located on the white pulp and red pulp. E, F) Meningeal tissue from case 1: E) mononuclear meningoencephalitis (arrow); F) YF antigens detected in the cytoplasm of meningeal inflammatory cells. G, H) Cardiac tissue from case 1: G) mononuclear interstitial myocarditis (arrow); H) positive YF antigens detected in the inflammatory cells; I, J) Kidney tissue from case 1: I) acute tubular necrosis and interstitial nephritis (arrow); J) detectable YF antigens in the inflammatory cells. K ,L) Liver tissue from case 2: K) steatotic hepatitis with rare apoptotic bodies (inset); L) scarce immunodetection of YF antigens in the Kuppfer cells. Panels A, C, D, E, G, I, and K are hematoxylin and eosin stained; B, D, F, H, J, and L are immunohistochemistry with alkaline phosphatase conjugated polymer, using a mouse polyclonal YF antibody directed to wild strain (Instituto Adolfo Lutz, São Paolo, Brazil). Scale bars in panels A, C, E, and G indicate 50 µm and in panel K indicates 20 µm. Original magnification ×400.