Volume 29, Number 3—March 2023
Research Letter
Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Pregnant Woman and Long-Term Sequelae
Figure
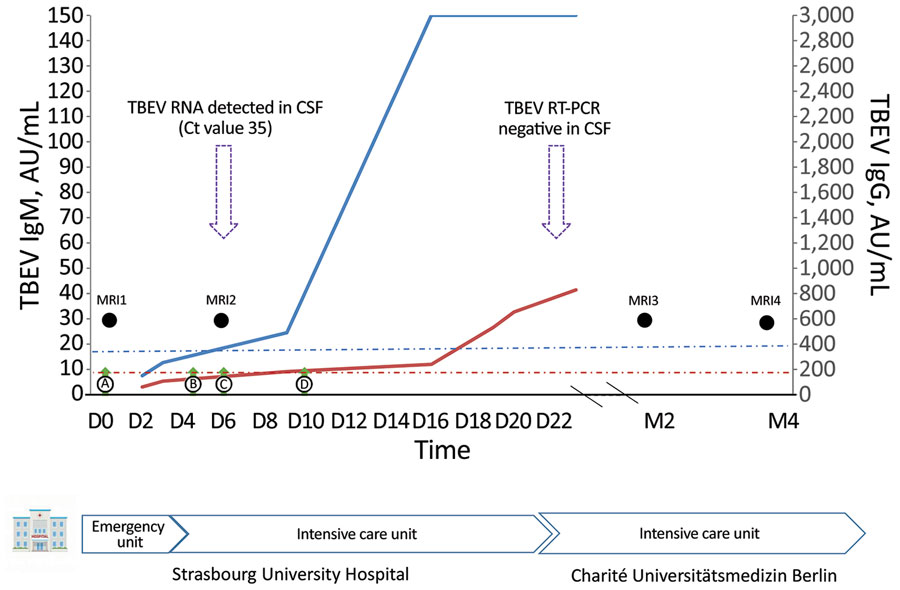
Figure. Tick-borne encephalitis in pregnant woman and long-term sequelae showing relevant clinical and laboratory findings, including TBEV antibody kinetics in serum samples. TBEV IgM (blue curve) and IgG (red curve) were detected in serum samples by using the Serion ELISA Classic TBE Virus IgG/IgM Kit (https://www.serion-immunologics.com) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Results are expressed in arbitrary units (AU) per milliliter, with a positive threshold of 15 AU/mL for IgM (blue dot-dash line) and 150 AU/mL for IgG (red dot-dash line). Green arrows indicate clinical findings; black circles indicate timing of MRIs; purple arrows indicate TBE real-time RT-PCR performed for CSF, with the Ct value for a positive result. An in-house RT-PCR for TBEV nucleic acid was performed on CSF samples. Primer and probe sequences targeted the 3′-untranslated region of the viral genome as described by Cassinoti and Swchaiger (2). A positive control, a negative control, and an internal control were included to monitor overall efficiency of the RT-PCR. CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; Ct, cycle threshold; D, day after admission; M, month after admission; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-PCR; TBEV, tick-borne encephalitis virus.
References
- Velay A, Paz M, Cesbron M, Gantner P, Solis M, Soulier E, et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus: molecular determinants of neuropathogenesis of an emerging pathogen. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019;45:472–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schwaiger M, Cassinotti P. Development of a quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay with internal control for the laboratory detection of tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) RNA. J Clin Virol. 2003;27:136–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weinmayr LM, Kanz D, Eckenweiler M, Bormann T, Huzly D, Bardutzky J, et al. Acute tick-borne encephalitis during pregnancy - An alarming combination. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020;11:
101512 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Divé I, Veje M, Dobler G, Bergström T, Buxmann H, Paul B, et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) infection in pregnancy: Absence of virus transmission to the fetuses despite severe maternal disease - A case study. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020;11:
101491 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Charlier C, Beaudoin M-C, Couderc T, Lortholary O, Lecuit M. Arboviruses and pregnancy: maternal, fetal, and neonatal effects. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2017;1:134–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bakhvalova VN, Potapova OF, Panov VV, Morozova OV. Vertical transmission of tick-borne encephalitis virus between generations of adapted reservoir small rodents. Virus Res. 2009;140:172–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taba P, Schmutzhard E, Forsberg P, Lutsar I, Ljøstad U, Mygland Å, et al. EAN consensus review on prevention, diagnosis and management of tick-borne encephalitis. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:1214–e61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lipowski D, Popiel M, Perlejewski K, Nakamura S, Bukowska-Osko I, Rzadkiewicz E, et al. A cluster of fatal tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in organ transplant setting. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:896–901. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Silasi M, Cardenas I, Kwon J-Y, Racicot K, Aldo P, Mor G. Viral infections during pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2015;73:199–213. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Blom K, Cuapio A, Sandberg JT, Varnaite R, Michaëlsson J, Björkström NK, et al. Cell-mediated immune responses and immunopathogenesis of human tick-borne encephalitis virus-infection. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2174. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar