Volume 29, Number 4—April 2023
Dispatch
Yezo Virus Infection in Tick-Bitten Patient and Ticks, Northeastern China
Figure 2
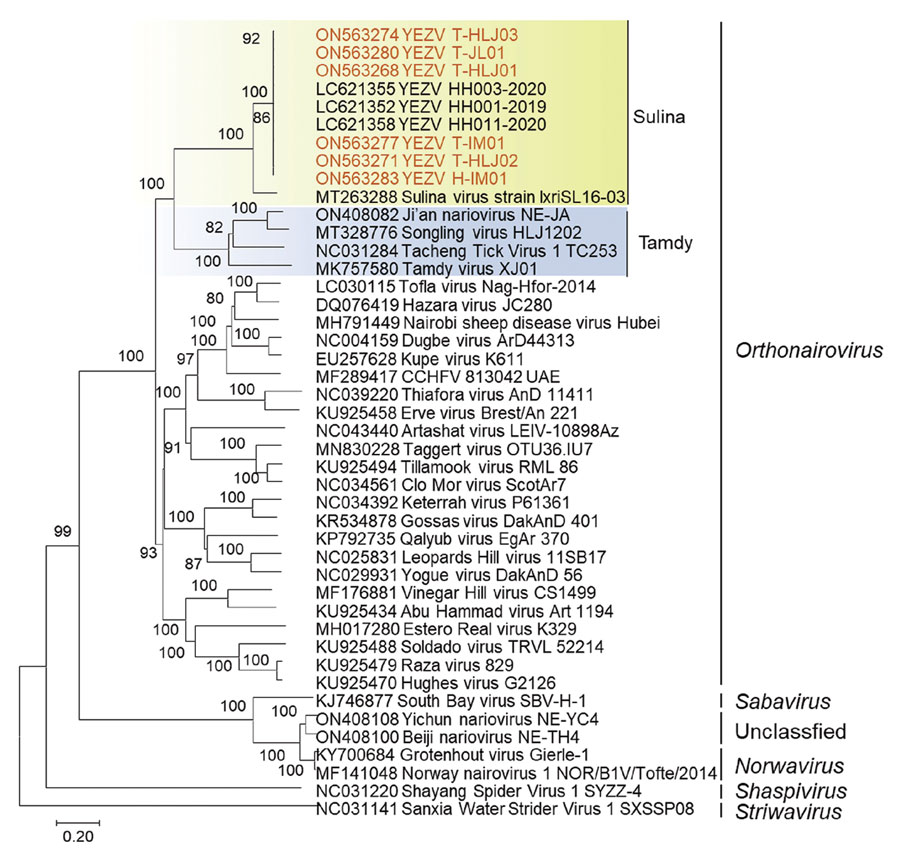
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analyses of Yezo virus from a tick-bitten person and Ixodes persulcatus ticks, northeastern China (red text), and references viruses. Sequences of representative viral strains were downloaded from National Center for Biotechnology Information public databases (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) and aligned together using MEGA version 7.0 (https://www.megasoftware.net). A bootstrapping analysis of 1,000 replicates were conducted, and values >70 were considered significant and are shown. Shading indicates Sulin virus genogroup strains (green) and Tamdy virus strain (blue). Numbers along branches are bootstrap values. Scale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: January 28, 2023
Page updated: March 21, 2023
Page reviewed: March 21, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.