Volume 29, Number 4—April 2023
Synopsis
Bacterial Agents Detected in 418 Ticks Removed from Humans during 2014–2021, France
Figure 2
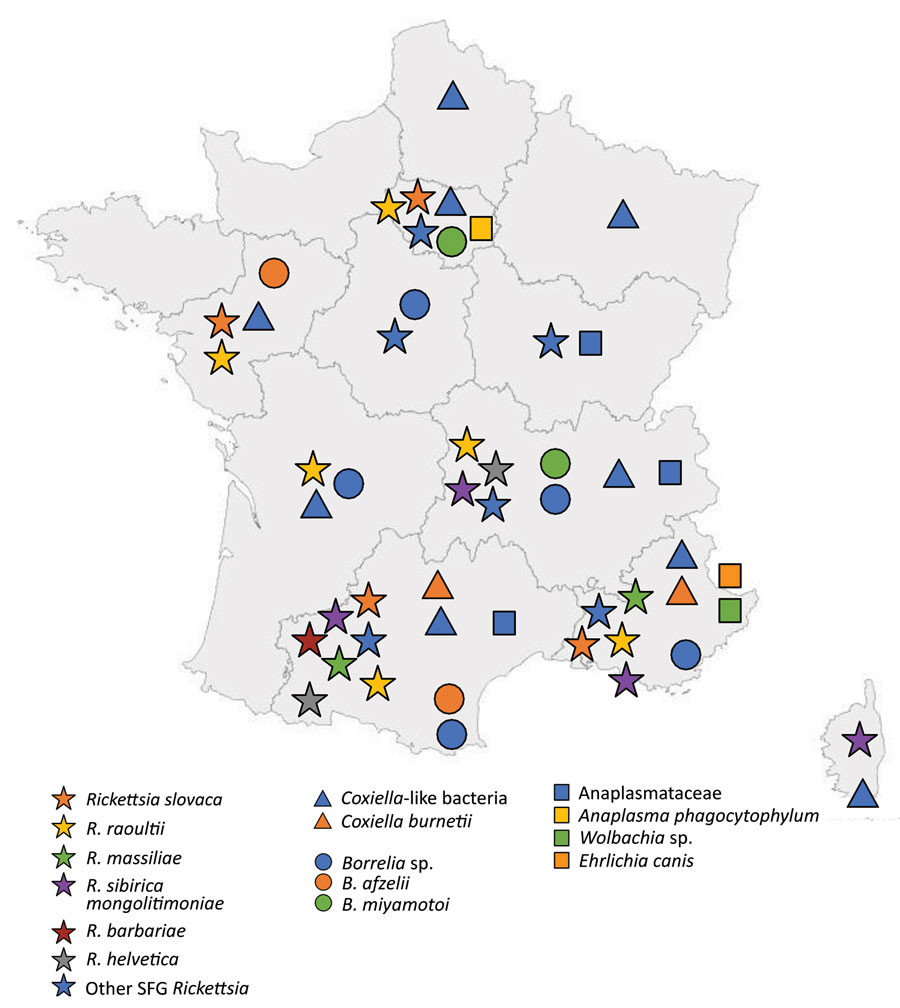
Figure 2. Geographic origin of ticks and identification of tickborne bacteria in study of bacterial agents detected in 418 ticks removed from humans during 2014–2021, France. Symbols indicate tick species and tickborne bacteria identified from locations in metropolitan France, including Corsica. Ticks were sent to the Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection in Marseille, France, and identified by using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Bacteria carried by the ticks were isolated and identified by PCR or serologic methods at the institute. Of the ticks evaluated, 387 were from metropolitan France; 3 from Guadeloupe, a territory of France in the West Indies; and 28 from other countries.