Volume 29, Number 4—April 2023
Research Letter
Harbor Porpoise Deaths Associated with Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, the Netherlands, 2021
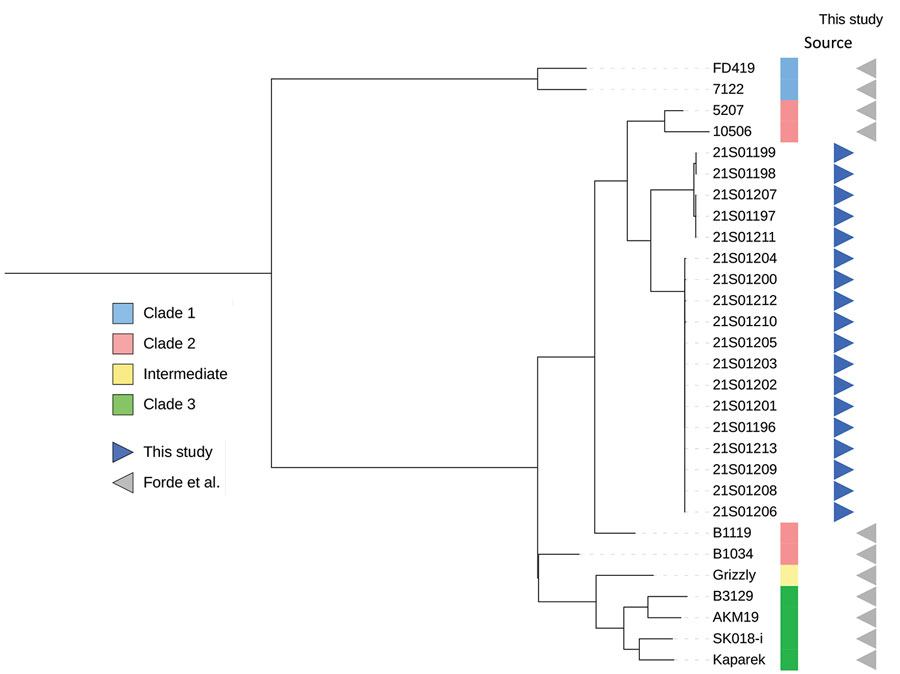
Figure
References
- Wang Q, Chang BJ, Riley TV. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Vet Microbiol. 2010;140:405–17. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ceccolini ME, Wessels M, Macgregor SK, Deaville R, Perkins M, Jepson PD, et al. Systemic Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in seven free-ranging delphinids stranded in England and Wales. Dis Aquat Organ. 2021;145:173–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- IJsseldijk LL, Brownlow AC, Mazzariol S, editors. Best practice for cetacean post mortem investigation and tissue sampling. Joint ACCOBAMS and ASCOBANS document. Stralsund, Germany: Agreement for the Conservation of Cetaceans of the Baltic Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area (ACCOBAMS); Agreement on the Conservation of Small Cetaceans of the Baltic, North East Atlantic, Irish and North Seas (ASCOBANS); 2019 [cited 2022 Nov 7]. https://www.ascobans.org/sites/default/files/document/ascobans_ac25_inf3.2_rev1_best-practice-cetacean-post-mortem-investigation.pdf
- Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19:455–77. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Forde T, Biek R, Zadoks R, Workentine ML, De Buck J, Kutz S, et al. Genomic analysis of the multi-host pathogen Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae reveals extensive recombination as well as the existence of three generalist clades with wide geographic distribution. BMC Genomics. 2016;17:461. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Treangen TJ, Ondov BD, Koren S, Phillippy AM. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol. 2014;15:524. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W256–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Briese T, Kapoor A, Mishra N, Jain K, Kumar A, Jabado OJ, et al. Virome capture sequencing enables sensitive viral diagnosis and comprehensive virome analysis. MBio. 2015;6:e01491–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Elk C, van de Bildt M, van Run P, de Jong A, Getu S, Verjans G, et al. Central nervous system disease and genital disease in harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) are associated with different herpesviruses. Vet Res (Faisalabad). 2016;47:28. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brooke CJ, Riley TV. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: bacteriology, epidemiology and clinical manifestations of an occupational pathogen. J Med Microbiol. 1999;48:789–99. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 08, 2023
Page updated: March 21, 2023
Page reviewed: March 21, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.