Volume 29, Number 5—May 2023
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Emergence of Erythromycin-Resistant Invasive Group A Streptococcus, West Virginia, USA, 2020–2021
Figure 3
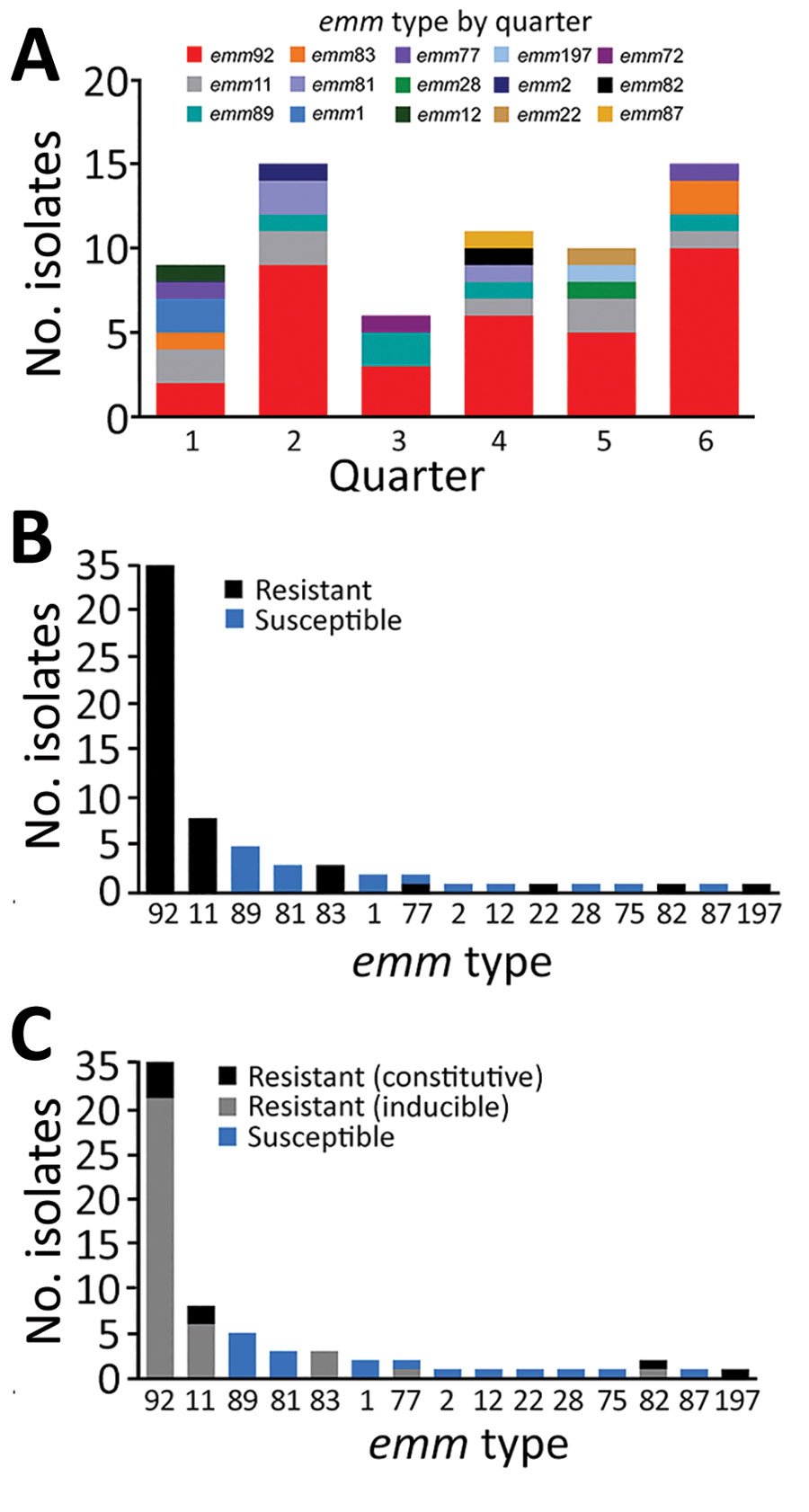
Figure 3. emm type distribution and MLSB resistance among invasive group A Streptococcus isolates, West Virginia, USA, 2020–2021. A) Temporal analysis of isolate emm type by 3-month periods. Specimens harboring isolates were collected during January 2020–June 2021, represented by consecutive quarters numbered 1–6. Graph indicates trend of emm92 isolates predominating each quarter over the study period. B, C) MLSB susceptibility and resistance profiles. The number of isolates resistant to erythromycin (B) and clindamycin (C) by emm type was determined on the basis of antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Isolates were deemed nonsusceptible to clindamycin if they had either an inducible or constitutive resistance phenotype and deemed susceptible in the absence of growth as determined by D-test.
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.