Volume 29, Number 5—May 2023
Dispatch
Rustrela Virus as Putative Cause of Nonsuppurative Meningoencephalitis in Lions
Figure 1
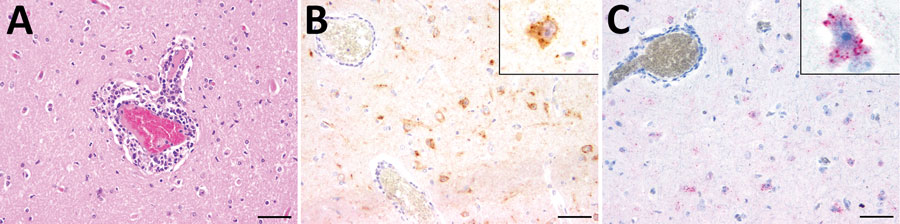
Figure 1. Histopathologic, immunohistochemical, and in situ hybridization findings in the cerebrum of a lion tested positive for rustrela virus (RusV) by quantitative reverse transcription PCR. A) Histopathologic analysis of cerebral sample from lion 3 indicated lymphohistiocytic meningoencephalitis and vasculitis. B) Immunohistochemistry analysis showed RusV antigen in cortical neurons and their processes. Cytoplasmic granular immunoreactivity is visible (inset). C) In situ hybridization revealed RusV RNA in cortical neurons; we observed cytoplasmic granular-positive signal (inset). Scale bars indicate 50 µm.
Page created: April 04, 2023
Page updated: April 19, 2023
Page reviewed: April 19, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.