Volume 3, Number 1—March 1997
Dispatch
Isolation and Phylogenetic Characterization of Ebola Viruses Causing Different Outbreaks in Gabon
Figure 2
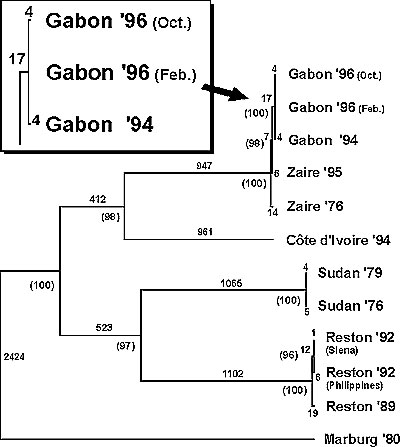
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between the Ebola viruses that caused outbreaks of disease in Gabon and previously described filoviruses (5). The entire coding region for the glycoprotein gene of the viruses shown was used in maximum parsimony analysis, and a single most parsimonious tree was obtained. Numbers in parentheses indicate bootstrap confidence values for branch points and were generated from 500 replicates (heuristic search). Branch length values are also shown.
References
- Cox NJ, McCormick JB, Johnson KM, Kiley MP. Evidence for two subtypes of Ebola virus based on oligonucleotide mapping of RNA. J Infect Dis. 1983;147:272–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fisher-Hoch SP, Brammer TL, Trappier SG, Hutwagner LC, Farrar BB, Ruo SL, Pathogenic potential of filoviruses: role of geographic origin of primate host and virus strain. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:753–63.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jahrling PB, Geisbert TW, Jaax NK, Hanes MA, Ksiazek TG, Peters CJ. Experimental infection of cynomolgus macaques with Ebola-Reston filoviruses from the 1989-1990 US epizootic. Arch Virol. 1996;11(Suppl):115–34.
- Peters CJ, Sanchez A, Rollin PE, Ksiazek TG, Murphy F. Filoviridae: Marburg and Ebola viruses. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Virology, 3rd ed., Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers,1996:1161-76.
- Sanchez A, Trappier SG, Mahy BWJ, Peters CJ, Nichol ST. The virion glycoproteins of Ebola viruses are encoded in two reading frames and are expressed through transcriptional editing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:3602–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ivanoff B, Duquesnoy P, Languillat G, Saluzzo J-F, Georges A, Gonzalez J-P, Haemorrhagic fever in Gabon. I. Incidence of Lassa, Ebola and Marburg viruses in Haut-Ogooué. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76:719–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Georges AJ, Renaut AA, Bertherat E, Baize S, Leroy E, LeGuenno B, Recent Ebola virus outbreaks in Gabon from 1994 to 1996: epidemiologic and control issues. Proceedings of the International Colloquium on Ebola Virus Research; 1996 Sept 4-7; Antwerp, Belgium.
- World Health Organization. Outbreak of Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Gabon officially declared over. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 1996;71:125–6.
- World Health Organization. Ebola haemorrhagic fever—Gabon. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 1996;71:320.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Ebola haemorrhagic fever-South Africa. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 1996;71:359.
- World Health Organization. Ebola haemorrhagic fever. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 1997;72:7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swofford DL. 1991. PAUP: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, version 3.1.1. Champaign (IL): Illinois Natural History Survey.
- Zaki SR, Greer PW, Goldsmith CS, Coffield LM, Rollin PE, Callain P, Ebola virus hemorrhagic fever: pathologic, immunopathologic and ultrastructural studies. Proceedings of the International Colloquium on Ebola Virus Research; 1996 Sept 4-7; Antwerp, Belgium.
- Lloyd E, Zaki SR, Rollin PE. Long term surveillance for Ebola in Zaire. Proceedings of the International Colloquium on Ebola Virus Research; 1996 Sept 4-7; Antwerp, Belgium.
- LeGuenno B, Formenty P, Wyers M, Gounon P, Walker F, Boesch C. Isolation and partial characterization of a new strain of Ebola virus. Lancet. 1995;345:1271–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 21, 2010
Page updated: December 21, 2010
Page reviewed: December 21, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.