Volume 30, Number 1—January 2024
Dispatch
Hantavirus Disease Cluster Caused by Seoul Virus, Germany
Figure
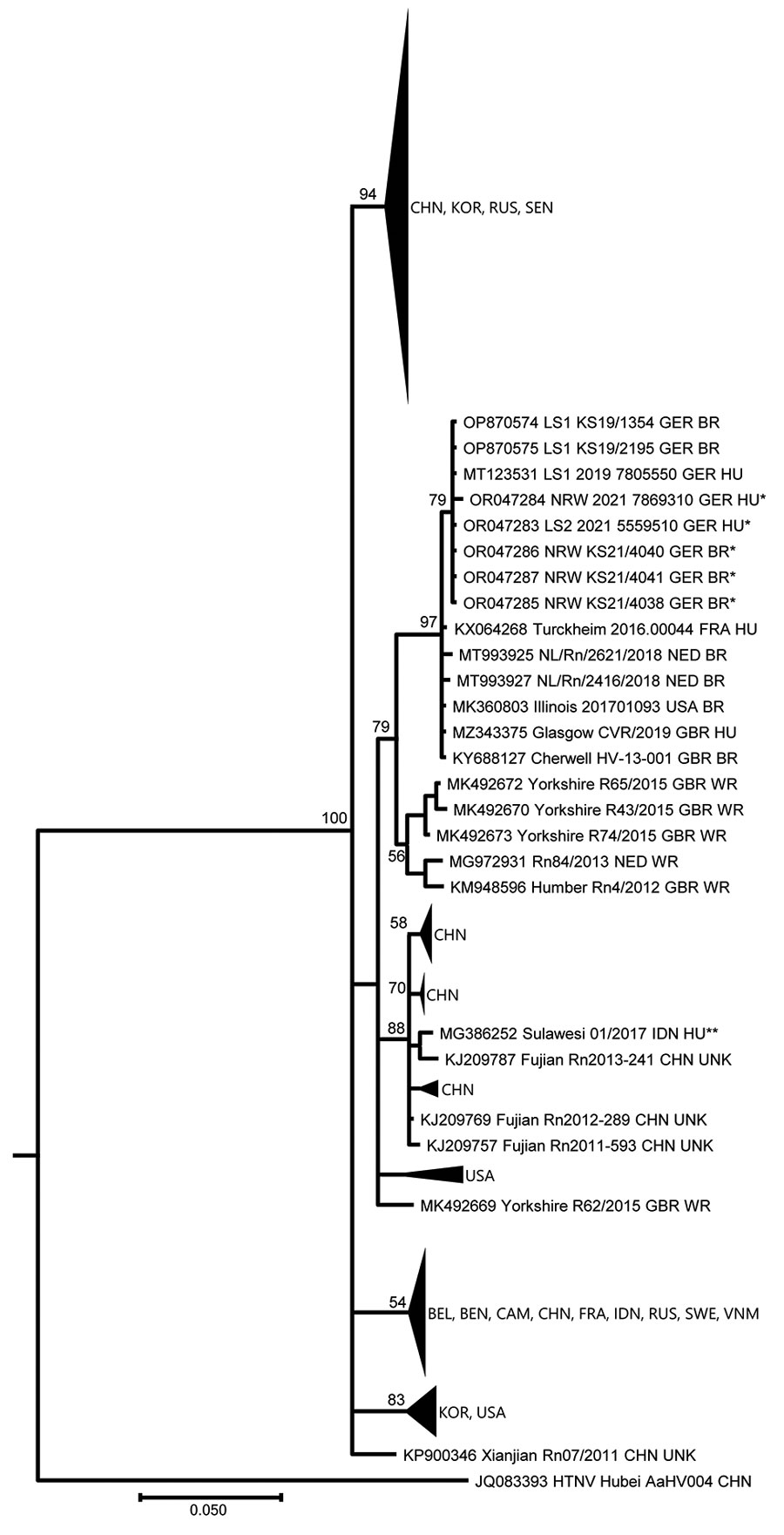
Figure. Phylogenetic tree of partial large segment Seoul virus sequences from humans and rats, Germany. Segments were 412-nt long, positions nt 2919–3330 based on reference sequence (KM948594_Cherwell_GBR_BR). The partial large segment Bayesian tree was reconstructed using 20 million generations and the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano substitution model with gamma distribution and invariant sites. Single asterisks indicate sequences from this study, denoted by their GenBank accession numbers. Double asterisks indicate sequence from the imported Seoul virus case from Indonesia (9). Aa, Apodemus agrarius; BEL, Belgium; BEN, Benin; BR, breeder rat (includes feeder, lab, and pet rats); CAM, Cambodia; CHN, China; FRA, France; GBR, Great Britain; GER, Germany; HTNV, Hantaan virus; HU, human; IDN, Indonesia; KOR, Korea; L, large segment; NED, the Netherlands; Rn, Rattus norvegicus; RUS, Russia; SEN, Senegal; SEOV, Seoul virus; SWE, Sweden; UNK, unknown wild or breeder rat; USA, United States of America; VNM, Vietnam; WR, wild rat.
References
- Kruger DH, Figueiredo LT, Song JW, Klempa B. Hantaviruses—globally emerging pathogens. J Clin Virol. 2015;64:128–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee HW. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Korea. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11(Suppl 4):S864–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clement J, LeDuc JW, McElhinney LM, Reynes JM, Van Ranst M, Calisher CH. Clinical characteristics of ratborne Seoul hantavirus disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25:387–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hofmann J, Heuser E, Weiss S, Tenner B, Schoppmeyer K, Esser J, et al. Autochthonous ratborne Seoul virus infection in woman with acute kidney injury. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:3096–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhang YZ, Dong X, Li X, Ma C, Xiong HP, Yan GJ, et al. Seoul virus and hantavirus disease, Shenyang, People’s Republic of China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:200–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clement J, LeDuc JW, Lloyd G, Reynes JM, McElhinney L, Van Ranst M, et al. Wild rats, laboratory rats, pet rats: global Seoul hantavirus disease revisited. Viruses. 2019;11:652. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Heuser E, Drewes S, Trimpert J, Kunec D, Mehl C, de Cock MP, et al. Pet rats as the likely reservoir for human Seoul orthohantavirus infection. Viruses. 2023;15:467. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Klempa B, Fichet-Calvet E, Lecompte E, Auste B, Aniskin V, Meisel H, et al. Hantavirus in African wood mouse, Guinea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:838–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hofmann J, Weiss S, Kuhns M, Zinke A, Heinsberger H, Kruger DH. Importation of human Seoul virus infection to Germany from Indonesia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018;24:1099–102. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar