Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
Dispatch
Toxoplasma gondii Infections and Associated Factors in Female Children and Adolescents, Germany
Figure 1
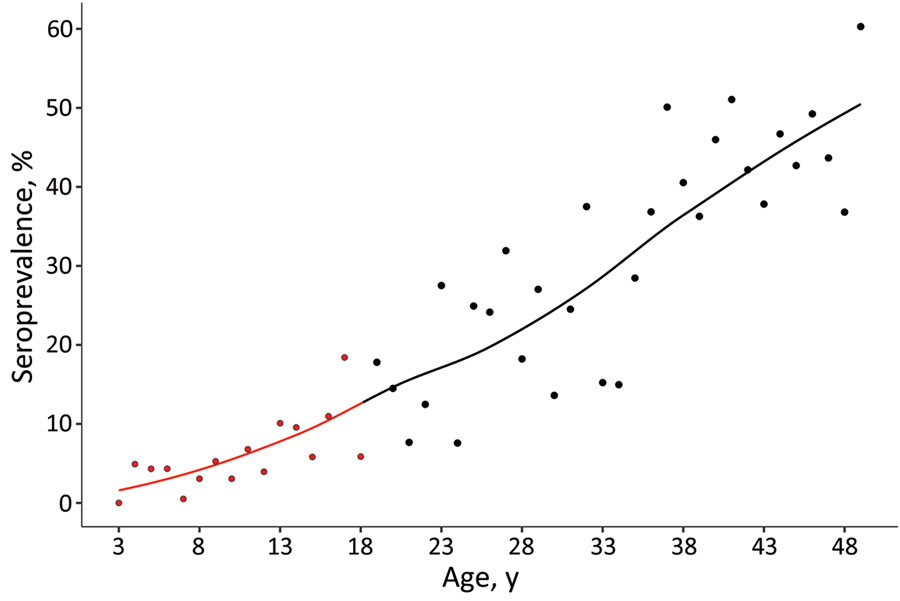
Figure 1. Weighted seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infections in female children and adolescents by age, Germany, 2014–2017 (red). For comparison, results of Wilking et al. (3), a previous study among adults, were added to the graph (black)
References
- Wilking H, Thamm M, Stark K, Aebischer T, Seeber F. Prevalence, incidence estimations, and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii infection in Germany: a representative, cross-sectional, serological study. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22551. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pleyer U, Gross U, Schlüter D, Wilking H, Seeber F. Toxoplasmosis in Germany. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019;116:435–44.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Koutsoumanis K, Allende A, Alvarez-Ordóñez A, Bolton D, Bover-Cid S, Chemaly M, et al.; EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Public health risks associated with food-borne parasites. EFSA J. 2018;16:
e05495 .PubMedGoogle Scholar - Lampert T, Hoebel J, Kuntz B, Müters S, Kroll LE. Socioeconomic status and subjective social status measurement in KiGGS Wave 2. J Health Monit. 2018;3:108–25.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Murat JB, Dard C, Fricker Hidalgo H, Dardé ML, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Pelloux H. Comparison of the Vidas system and two recent fully automated assays for diagnosis and follow-up of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women and newborns. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013;20:1203–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Candela MG, Fanelli A, Carvalho J, Serrano E, Domenech G, Alonso F, et al. Urban landscape and infection risk in free-roaming cats. Zoonoses Public Health. 2022;69:295–311. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pacheco-Ortega GA, Chan-Pérez JI, Ortega-Pacheco A, Guzmán-Marín E, Edwards M, Brown MA, et al. Screening of zoonotic parasites in playground sandboxes of public parks from subtropical Mexico. J Parasitol Res. 2019;2019:
7409076 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Hofhuis A, van Pelt W, van Duynhoven YTHP, Nijhuis CDM, Mollema L, van der Klis FRM, et al. Decreased prevalence and age-specific risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii IgG antibodies in The Netherlands between 1995/1996 and 2006/2007. Epidemiol Infect. 2011;139:530–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sharif M, Daryani A, Barzegar G, Nasrolahei M. A seroepidemiological survey for toxoplasmosis among schoolchildren of Sari, Northern Iran. Trop Biomed. 2010;27:220–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nash JQ, Chissel S, Jones J, Warburton F, Verlander NQ. Risk factors for toxoplasmosis in pregnant women in Kent, United Kingdom. Epidemiol Infect. 2005;133:475–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jones JL, Kruszon-Moran D, Elder S, Rivera HN, Press C, Montoya JG, et al. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in the United States, 2011-2014. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98:551–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fan CK, Lee LW, Liao CW, Huang YC, Lee YL, Chang YT, et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection: relationship between seroprevalence and risk factors among primary schoolchildren in the capital areas of Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe, West Africa. Parasit Vectors. 2012;5:141. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liassides M, Christodoulou V, Moschandreas J, Karagiannis C, Mitis G, Koliou M, et al. Toxoplasmosis in female high school students, pregnant women and ruminants in Cyprus. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2016;110:359–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cabral Monica T, Evers F, de Souza Lima Nino B, Pinto-Ferreira F, Breganó JW, Ragassi Urbano M, et al. Socioeconomic factors associated with infection by Toxoplasma gondii and Toxocara canis in children. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022;69:1589–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang S, Yao Z, Li H, Li P, Wang D, Zhang H, et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii infection in primary school children in Henan province, central China. Parasite. 2020;27:23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: March 22, 2024
Page updated: April 24, 2024
Page reviewed: April 24, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.