Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
Research
Kinetics of Hepatitis E Virus Infections in Asymptomatic Persons
Figure 1
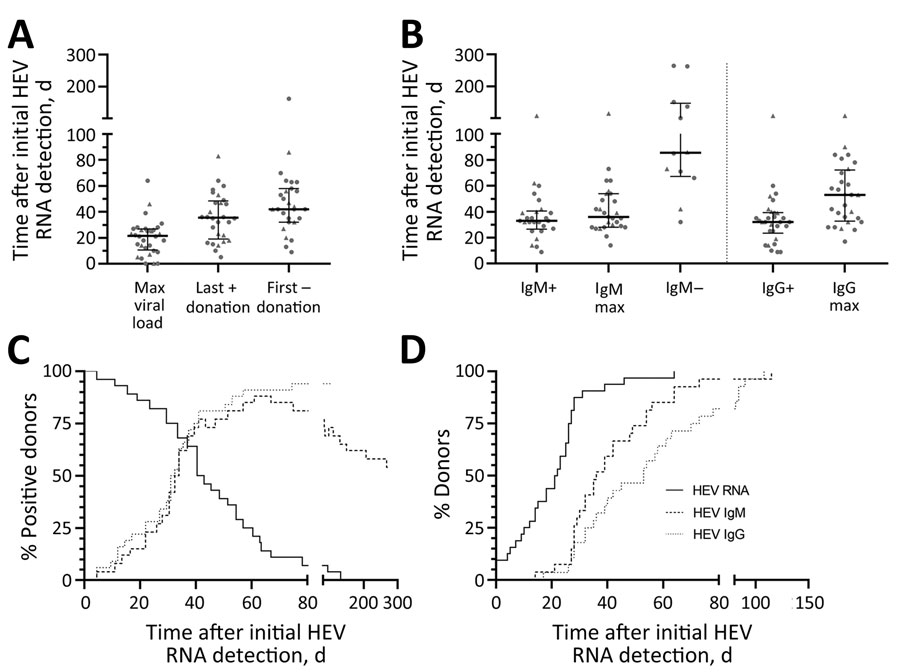
Figure 1. Progression of HEV infection in asymptomatic persons determined from retrospectively tested blood samples, Germany. A) Days at which the maximum viral load was reached as well as the time points of last HEV RNA–positive and the first HEV RNA–negative donation. B) Serostatus for HEV IgM and HEV IgG revealing the time points of primary HEV IgM or IgG detection, maximum ratio signal to cutoff, and loss of detectability of HEV IgM. In panels A and B, data points indicate each person; error bars indicate medians with interquartile ranges; circles indicate donors who donated HEV-negative blood before first detection of HEV RNA; and triangles indicate persons who did not donate HEV-negative blood before first detection of HEV RNA. C) percentages of persons who were positive for the markers HEV RNA, HEV IgM, and HEV IgG. D) Progression curves for the percentages of persons in whom the maximum of those markers was exceeded, depending on the time since initial HEV RNA detection. HEV, hepatitis E virus; max, maximum; +, positive; –, negative.