Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
Research
Kinetics of Hepatitis E Virus Infections in Asymptomatic Persons
Figure 2
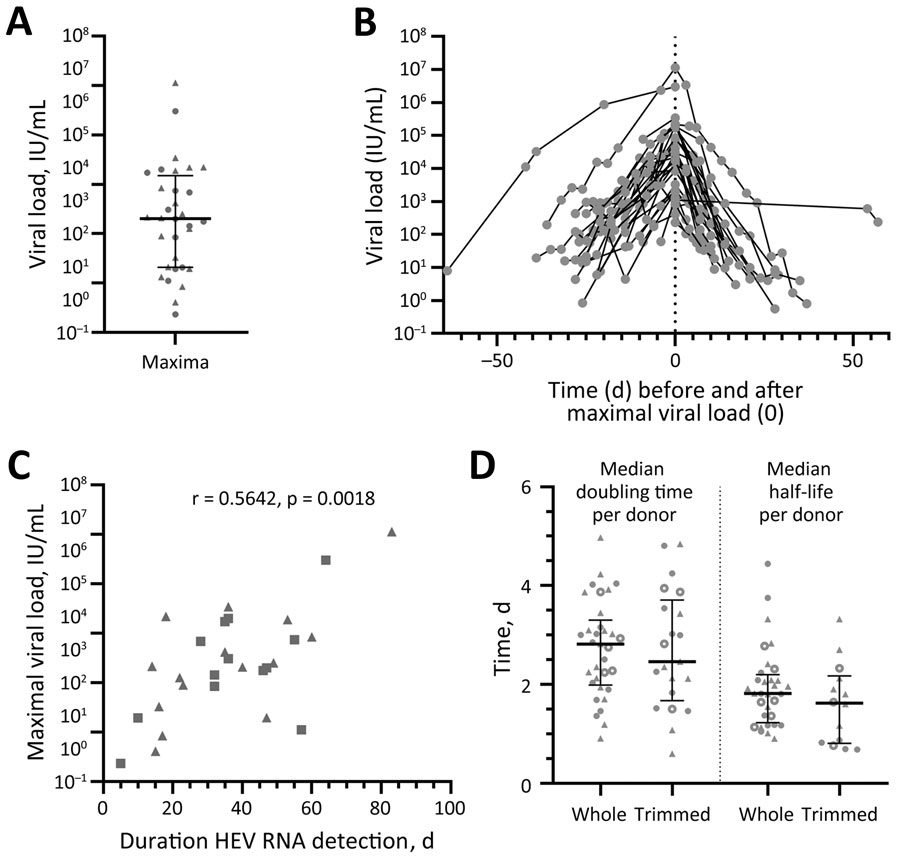
Figure 2. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) viral load in asymptomatic persons determined from retrospectively tested blood samples, Germany. A) Maximum viral load for each person (n = 32). B) Viral loads during the infection have been overlayed for all persons depending on the timepoint when the maximum viral load (set as day 0) was reached. C) Spearman coefficient calculated for the correlation of the maximum viral load and the duration of HEV RNA detection in the blood for persons with confirmed end of infection by HEV RNA–negative donation (n = 28). D) Doubling time was determined in the rising phase of the viral load, whereas the half-life was determined in the declining phase for the whole or a trimmed course. Data points indicate each person; error bars indicate medians with interquartile ranges; circles indicate donors who donated HEV-negative blood before first detection of HEV RNA (n = 14); and triangles indicate persons who did not donate HEV-negative blood before first detection of HEV RNA (n = 18). Data points calculated from data extracted from Vollmer et al. are displayed as open circles (n = 7) (21). HEV, hepatitis E virus.
References
- Cao D, Meng XJ. Molecular biology and replication of hepatitis E virus. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2012;1:
e17 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Purdy MA, Harrison TJ, Jameel S, Meng XJ, Okamoto H, Van der Poel WHM, et al.; Ictv Report Consortium. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Hepeviridae. J Gen Virol. 2017;98:2645–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Horvatits T, Varwig-Janssen D, Schulze Zur Wiesch J, Lübke R, Reucher S, Frerk S, et al. No link between male infertility and HEV genotype 3 infection. Gut. 2020;69:1150–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cheung CKM, Wong SH, Law AWH, Law MF. Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E: What we know so far? World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28:47–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Westhölter D, Hiller J, Denzer U, Polywka S, Ayuk F, Rybczynski M, et al. HEV-positive blood donations represent a relevant infection risk for immunosuppressed recipients. J Hepatol. 2018;69:36–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harvala H, Hewitt PE, Reynolds C, Pearson C, Haywood B, Tettmar KI, et al. Hepatitis E virus in blood donors in England, 2016 to 2017: from selective to universal screening. Euro Surveill. 2019;24:
1800386 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Aggarwal R, Jameel S, Hepatitis E. Hepatitis E. Hepatology. 2011;54:2218–26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis E [cited 2023 Jul 26]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e
- Pérez-Gracia MT, Suay B, Mateos-Lindemann ML. Hepatitis E: an emerging disease. Infect Genet Evol. 2014;22:40–59. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Federal Ministry of Justice. Announcement on the authorisation of medicinal products—defence against drug risks - order to test blood donors to prevent the transmission of hepatitis E virus through blood components for transfusion and stem cell preparations for haematopoietic reconstitution [in German] [cited 2023 Jul 26]. https://www.bundesanzeiger.de/pub/publication/8ziFMqlkUHaYCwHxuin?0
- Schoch S, Wälti M, Schemmerer M, Alexander R, Keiner B, Kralicek C, et al. Hepatitis A virus incidence rates and biomarker dynamics for plasma donors, United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27:2718–824. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whalley SA, Murray JM, Brown D, Webster GJM, Emery VC, Dusheiko GM, et al. Kinetics of acute hepatitis B virus infection in humans. J Exp Med. 2001;193:847–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Garcia-Retortillo M, Forns X, Feliu A, Moitinho E, Costa J, Navasa M, et al. Hepatitis C virus kinetics during and immediately after liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2002;35:680–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yoshikawa A, Gotanda Y, Itabashi M, Minegishi K, Kanemitsu K, Nishioka K. Hepatitis B NAT virus-positive blood donors in the early and late stages of HBV infection: analyses of the window period and kinetics of HBV DNA. Vox Sang. 2005;88:77–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Velavan TP, Pallerla SR, Johne R, Todt D, Steinmann E, Schemmerer M, et al. Hepatitis E: An update on One Health and clinical medicine. Liver Int. 2021;41:1462–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huang S, Zhang X, Jiang H, Yan Q, Ai X, Wang Y, et al. Profile of acute infectious markers in sporadic hepatitis E. PLoS One. 2010;5:
e13560 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Zhang J, Ge SX, Huang GY, Li SW, He ZQ, Wang YB, et al. Evaluation of antibody-based and nucleic acid-based assays for diagnosis of hepatitis E virus infection in a rhesus monkey model. J Med Virol. 2003;71:518–26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clayson ET, Myint KSA, Snitbhan R, Vaughn DW, Innis BL, Chan L, et al. Viremia, fecal shedding, and IgM and IgG responses in patients with hepatitis E. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:927–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hoofnagle JH, Nelson KE, Purcell RH, Hepatitis E. Hepatitis E. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1237–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vollmer T, Diekmann J, Johne R, Eberhardt M, Knabbe C, Dreier J. Novel approach for detection of hepatitis E virus infection in German blood donors. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:2708–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vollmer T, Diekmann J, Eberhardt M, Knabbe C, Dreier J. Hepatitis E in blood donors: investigation of the natural course of asymptomatic infection, Germany, 2011. Euro Surveill. 2016;21:30332. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pischke S, Behrendt P, Bock CT, Jilg W, Manns MP, Wedemeyer H. Hepatitis E in Germany—an under-reported infectious disease. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2014;111:577–83.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Faber M, Willrich N, Schemmerer M, Rauh C, Kuhnert R, Stark K, et al. Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence, seroincidence and seroreversion in the German adult population. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25:752–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ambrosioni J, Mamin A, Hadengue A, Bernimoulin M, Samii K, Landelle C, et al. Long-term hepatitis E viral load kinetics in an immunocompromised patient treated with ribavirin. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20:O718–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lhomme S, Kamar N, Nicot F, Ducos J, Bismuth M, Garrigue V, et al. Mutation in the hepatitis E virus polymerase and outcome of ribavirin therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;60:1608–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hofmann AF. Chemistry and enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Hepatology. 1984;4(Suppl):4S–14S. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller JFAP. Cellular basis of the immune response. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh). 1975;194(Supplement):55–76.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Perelson AS, Goldstein B, Rocklin S. Optimal strategies in immunology III. The IgM-IgG switch. J Math Biol. 1980;10:209–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pas SD, de Man RA, Mulders C, Balk AHMM, van Hal PTW, Weimar W, et al. Hepatitis E virus infection among solid organ transplant recipients, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:869–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tsiang M, Rooney JF, Toole JJ, Gibbs CS. Biphasic clearance kinetics of hepatitis B virus from patients during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Hepatology. 1999;29:1863–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar