Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Synopsis
Severe Human Parainfluenza Virus Community- and Healthcare-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults at Tertiary Hospital, Seoul, South Korea, 2010–2019
Figure 1
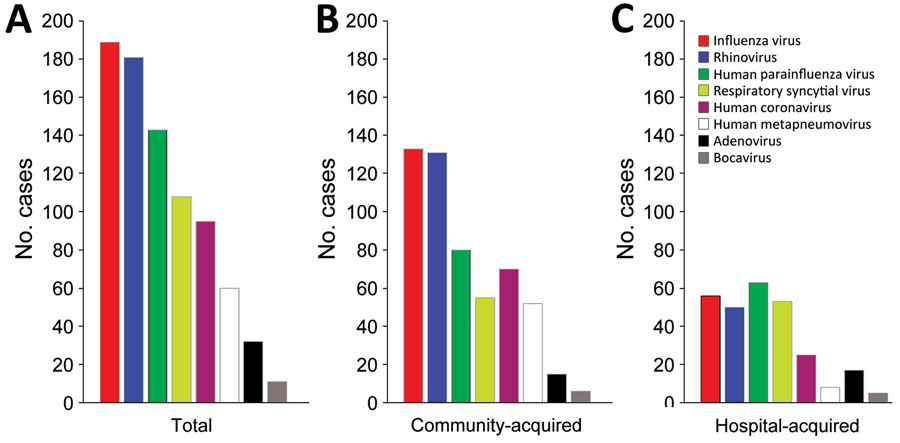
Figure 1. Prevalence of respiratory viruses in study of severe human parainfluenza virus community- and healthcare-acquired pneumonia in adults at a tertiary hospital in Seoul, South Korea, 2010–2019. Number of cases of different respiratory virus infections are given for 760 patients with severe pneumonia admitted to the intensive care unit at Asan Medical Center. A) Total number of patients with indicated virus infections. B) Number of patients with community-acquired virus infections. C) Number of patients with hospital-acquired virus infections.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: April 19, 2024
Page updated: May 22, 2024
Page reviewed: May 22, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.