Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Research
Incubation Period and Serial Interval of Mpox in 2022 Global Outbreak Compared with Historical Estimates
Figure 3
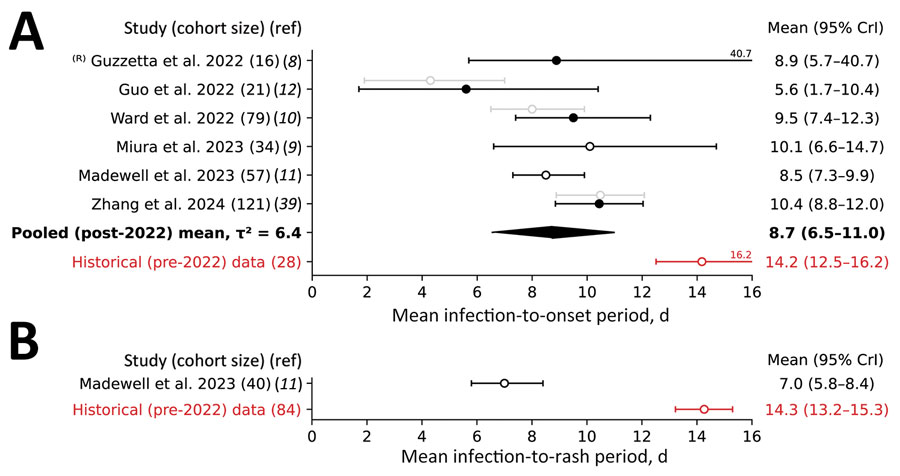
Figure 3. Forest plot of the estimated mean serial interval based on the date of symptom onset (A) and the date of rash onset (B) for studies conducted during the 2022–2023 global mpox outbreak and analyses of the historical case records. Open circles indicate analyses performed without adjusting for right truncation (ICC); solid circles indicate analyses when an adjustment was made (ICRTC). Whiskers indicate 95% CrI. Studies are denoted by the leading author and year of publication and ordered by their date of publication; the numbers in parentheses indicate the number of case records used for estimation. R) indicates that we re-evaluated estimates for consistency of the methods used. Gray indicates estimates not used for deriving the pooled mean, which is in bold text. Red indicates estimates for historical (pre‒2022 outbreak) data, indicating that they were not used for deriving the pooled mean. CrI, credible interval; ICC, interval censoring corrected model; ICRTC, interval censoring and right truncation corrected model; ref, reference; 2, -squared statistics indicating the between-study variance measured in days2.