Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Research
Estimates of SARS-CoV-2 Hospitalization and Fatality Rates in the Prevaccination Period, United States
Figure
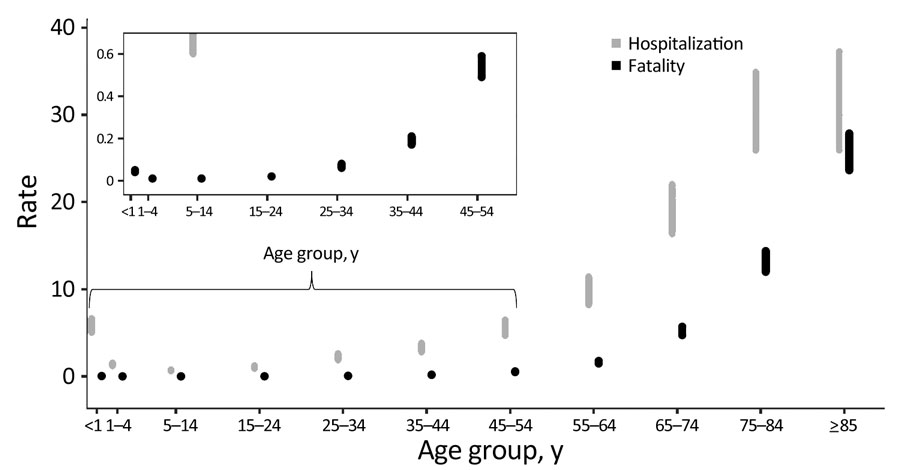
Figure. Upper and lower estimates of case-hospitalization (gray) and case-fatality (black) rates by age group of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, United States, 2020. Graphical representation of upper and lower estimates of rates in Tables 1 and 2. For case-hospitalization, lower bound was calculated by including cases with unknown hospitalization information as not hospitalized and upper bound by excluding cases with unknown hospitalization information. For case-fatality, lower bound was calculated by including cases with unknown death status as alive and upper bound by excluding cases with unknown death status information. Reports in which no response was provided about death or hospitalization were excluded from the respective rate calculation. Inset graph provides greater detail for younger age groups by using smaller y-axis values.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.