Volume 30, Number 7—July 2024
Research Letter
Fatal Infection in Ferrets after Ocular Inoculation with Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus
Figure 2
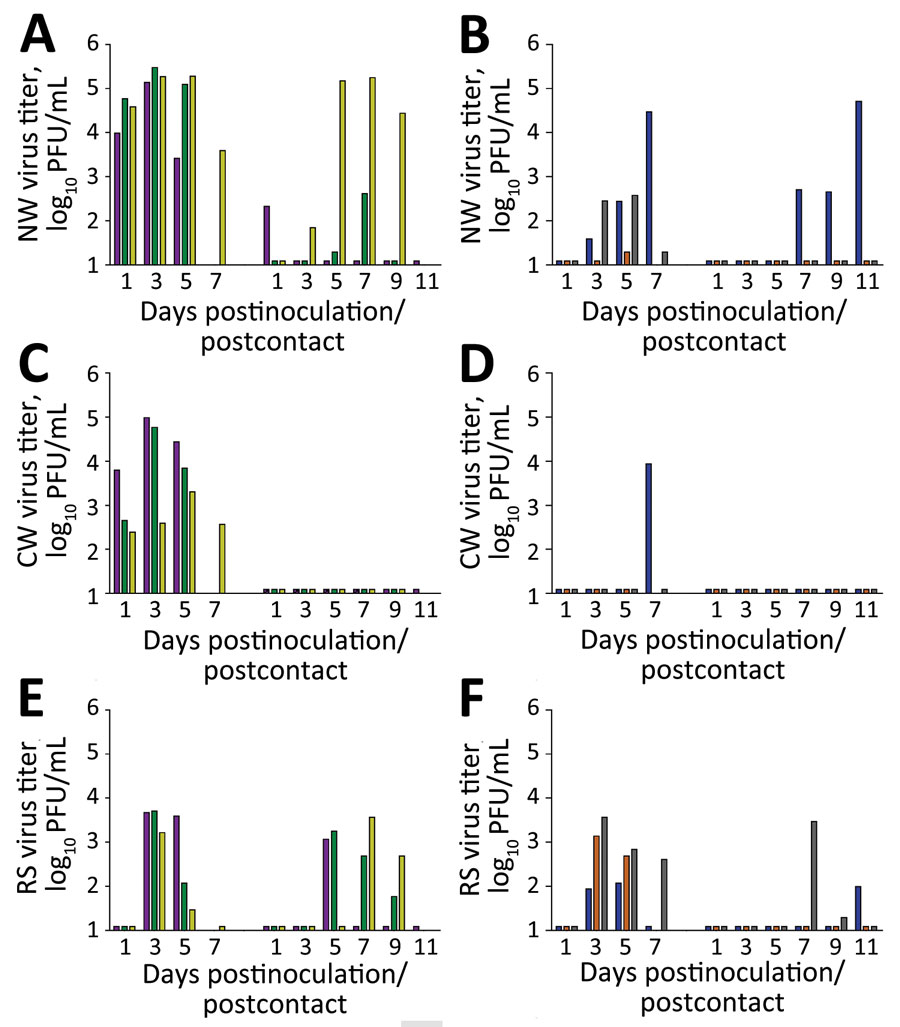
Figure 2. Transmission of Chile/25945 virus after ocular inoculation of ferrets. Ferrets were inoculated by the ocular route as previously described (7) with a high (106 PFU) or low (103 PFU) dose of Chile/25945 virus (100 μL), and each was cohoused with a serologically naive ferret 24 hours after inoculation. Specimens were collected from all ferrets as previously described (7) on alternate days after contact. A) NW specimen after ferret inoculation with 106 PFU challenge dose; B) NW specimen after inoculation with 103 PFU challenge dose; C) CW specimen after ferret inoculation with 106 PFU challenge dose; D) CW specimen after ferret inoculation with 103 PFU challenge dose; E) RS specimen after ferret inoculation with 106 PFU challenge dose; F) RS specimen after ferret inoculation with 103 PFU challenge dose. On each graph, left-hand bars indicate inoculated ferrets and right-hand bars indicate contact ferrets. Absence of a bar indicates an animal was humanely euthanized and no specimen was collected. Bar colors are linked with ferret morbidity data shown in [[ANCHOR###F1###Figure 1###Anchor]], panels A, B. Limit of detection was 10 PFU. CW, conjunctival wash/swab sample; NW, nasal wash sample; RS, rectal swab sample.