Volume 30, Number 8—August 2024
Research Letter
Panton-Valentine Leukocidin–Positive Staphylococcus aureus in Family and Pet Cat
Figure
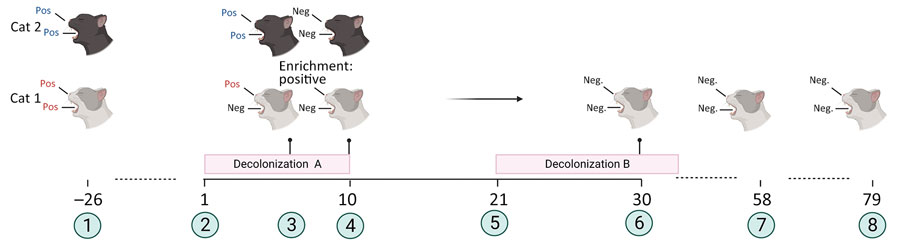
Figure. Timeline and overview of a successful decolonization attempt of 2 household cats colonized with methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, Germany. The family suffered from repeated soft-tissue infections caused by PVL-SA. Cat 1 was colonized with PVL-SA; cat 2 was colonized with PVL-negative SA. Decolonization period A consisted of oral administration of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid for 10 days. Decolonization period B consisted of parenteral administration of amoxicillin for 14 days. 1, initial screening for SA; 2, start of decolonization period A; 3, screening results at day 7 of decolonization period A; 4, screening results at day 10 of decolonization period A; 5, start of decolonization period B; 6, screening result of cat 1 during decolonization period B; 7, screening results on day 58 from the start of decolonization period A; 8, screening results on day 79 from the start of decolonization period A. Red text indicates positive for PVL-SA; blue text indicates positive for PVL-negative S. aureus. Figure created with Biorender (https://www.biorender.com; license BW 27.06.2023). Enrichment: Neg, negative for S. aureus; Pos, positive; Positive, positive for PVL-SA after enrichment step in liquid medium; PVL, Panton-Valentine leukocidin; PVL-SA, PVL-positive S. aureus.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.