Volume 30, Number 9—September 2024
Dispatch
Emergence of Extensively Drug-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, France, 2023
Figure
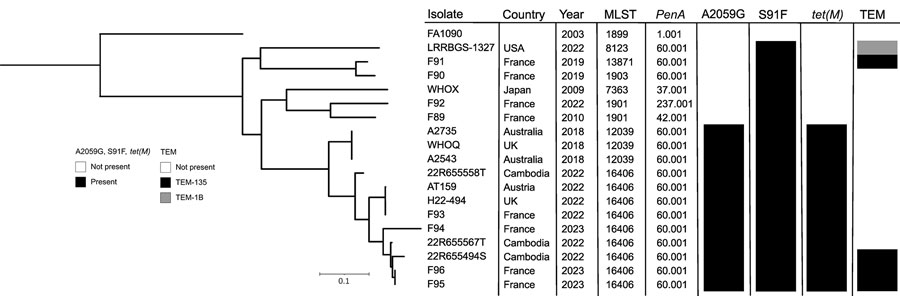
Figure. Phylogenetic tree of 19 Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates, including 2 from patients in France, compared on the basis of their main resistance determinants. The phylogenetic tree was built from 10,907 total core single-nucleotide polymorphism positions. The F95 and F96 isolates from 2 patients in France were compared with ceftriaxone-resistant and extensively drug-resistant N. gonorrhoeae isolates from Europe, Australia, Cambodia, Japan, and the United States. The tree is rooted on N. gonorrheae FA1090, a laboratory reference strain. Scale bar indicates the branch length corresponding to genetic change.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 12, 2024
Page updated: August 21, 2024
Page reviewed: August 21, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.