Detection and Genomic Characterization of Novel Mammarenavirus in European Hedgehogs, Italy
Barbara Di Martino

, Federica Di Profio, Maria Teresa Capucchio, Ilaria Prandi, Serena Robetto, Giuseppe Quaranta, Giuseppina La Rosa, Elisabetta Suffredini, Fulvio Marsilio, Vito Martella, and Vittorio Sarchese
Author affiliation: University of Teramo, Teramo, Italy (B. Di Martino, F. Di Profio, F. Marsilio, V. Sarchese); University of Turin, Grugliasco, Italy (M.T. Capucchio, I. Prandi, G. Quaranta); S.S. Patologie della Fauna Selvatica, Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale Piemonte, Liguria e Valle d'Aosta, Italy (S. Robetto); Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy (G. La Rosa, E. Suffredini); University of Bari Aldo Moro, Bari, Italy (V. Martella); University of Veterinary Medicine, Budapest, Hungary (V. Martella)
Main Article
Figure 3
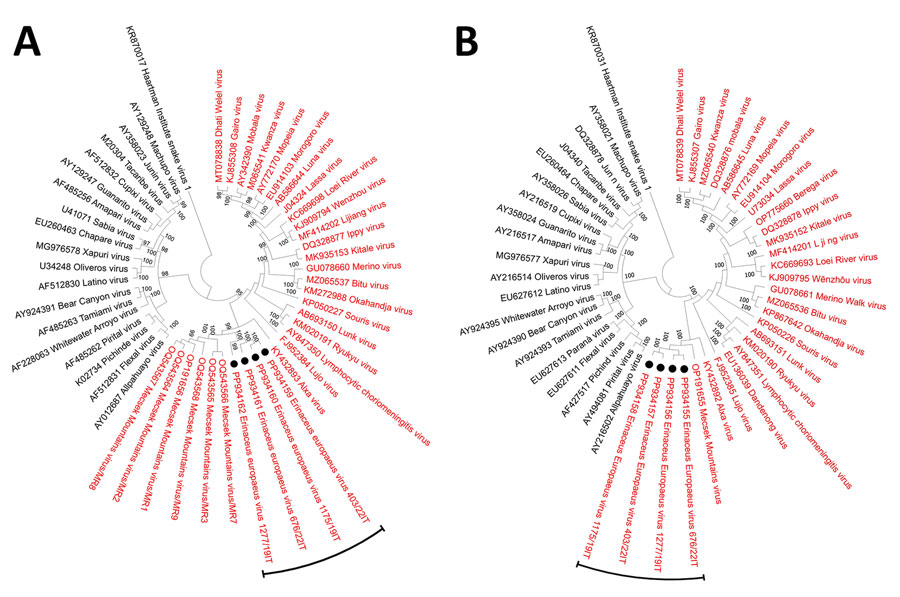
Figure 3. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analyses based on nucleotide sequences of the complete small (A) and large (B) segments of mammarenavirus strains identified in study of detection and genomic characterization of novel mammarenavirus in European hedgehogs, Italy, and prototype species currently classified within the genus Mammarenavirus. The evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. A total of 1,000 bootstrap replicates was used to estimate the robustness of the individual nodes on the phylogenetic tree. Black circles indicate the four Erinaceus europaeus hedgehog arenavirus strains (EEAV/676/22/IT, EEAV/1277/19/IT, EEAV/403/22/IT, and EEAV/1175/19/IT) detected in this study. In both trees, the Haartman Institute snake virus 1, representative of the genus Hartmanivirus, is used as an outgroup. GenBank accession numbers are provided.
Main Article
Page created: November 15, 2024
Page updated: December 22, 2024
Page reviewed: December 22, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
