Volume 31, Number 12—December 2025
Dispatch
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Virus Infection in Poultry Farm Workers, Washington, USA, 2024
Figure 1
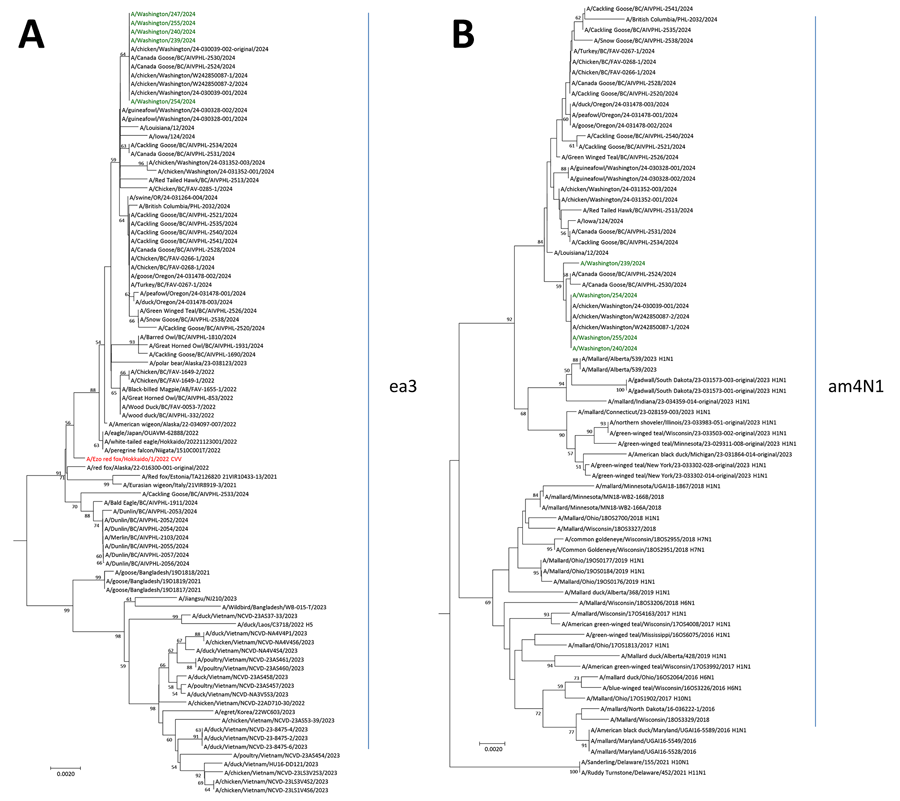
Figure 1. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b viruses isolated from poultry farm workers, Washington, USA, 2024. A) Hemagglutinin gene segment; B) neuraminidase gene segment. Green font indicates influenza A(H5N1) D1.1 viruses from Washington human cases; red font indicates prepandemic candidate vaccine virus A/Ezo red fox/Hokkaido/1/2022. Bootstrap values >50, generated from 1,000 replicates, are labeled on branch nodes. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: November 20, 2025
Page updated: January 01, 2026
Page reviewed: January 01, 2026
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.