Volume 31, Number 2—February 2025
Dispatch
Comparison of Contemporary and Historic Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Replication in Human Lung Organoids
Figure 1
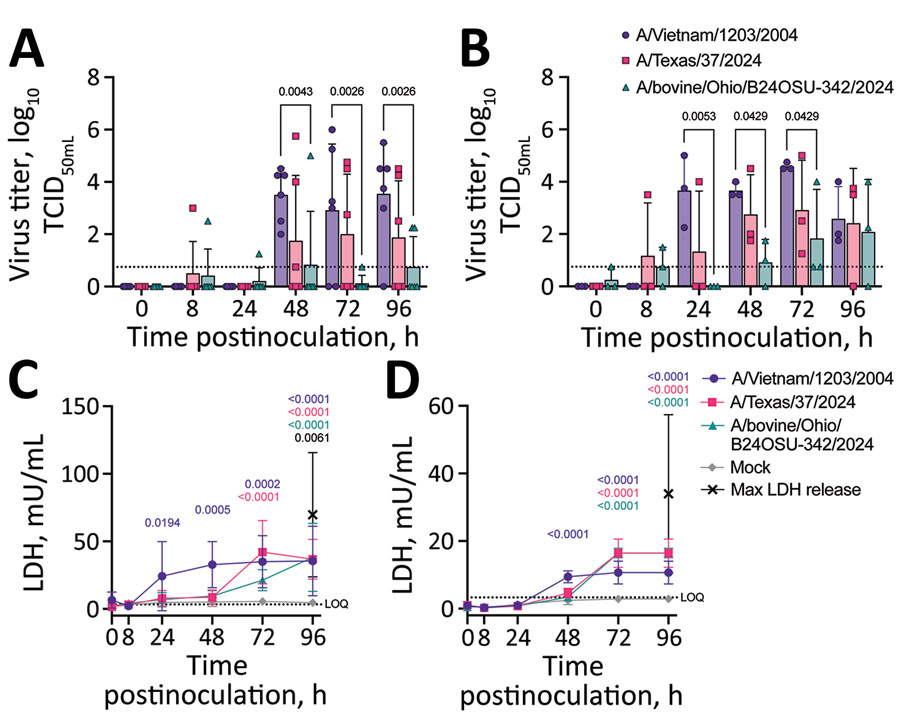
Figure 1. Virus replication and cytotoxicity in a comparison of contemporary and historic highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus replication in human lung organoids. A, B) Virus replication in ihLO (A) hLO (B). Cells were infected at a multiplicity of infection of 0.1 with 1 of the 3 indicated HPAI H5N1 virus isolates. Organoids were removed from Matrigel (Corning, https://www.corning.com) and incubated with virus for 1 hour at 37°C, after which virus was removed, organoids were washed, and replated in Matrigel. Culture supernatant samples were taken at 0, 8, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours postinoculation and titered on Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Titrations were read after 3 days by using a hemagglutination assay using turkey red blood cells. Dashed line indicates lower limit of detection; error bars denote means and SDs. p values <0.05 are indicated above bars. Of note, ihLOs and hLOs were derived from different donors. C,D) Cytotoxicity in ihLO (C) hLO (D). Culture supernatants from ihLOs (C) or hLOs (D) were collected and tested for release of lactate dehydrogenase into culture supernatant according to the LDH-Glo Cytotoxicity Assay protocol (Promega, https://www.promega.com) as an indicator of cell death. Results were converted to mU per mL LDH determined by the standard curve using a simple linear regression. Cells lysed with Triton X-100 (MilliporeSigma, https://www.sigmaaldrich.com) were included as maximum LDH release controls. Dashed line indicates lower limit of quantification. Error bars denote means and SDs of ihLO (n = 6 ) or hLO (n = 3) biologic replicates. Statistical analysis was conducted using 2-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey posttest. p values <0.05 are indicated and color coded by isolate. hLOs, adult stem cell–derived human lung organoids; HPAI, highly pathogenic avian influenza; ihLO, iPSC-derived human lung organoids; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.