Volume 31, Number 2—February 2025
Dispatch
Comparison of Contemporary and Historic Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Replication in Human Lung Organoids
Figure 3
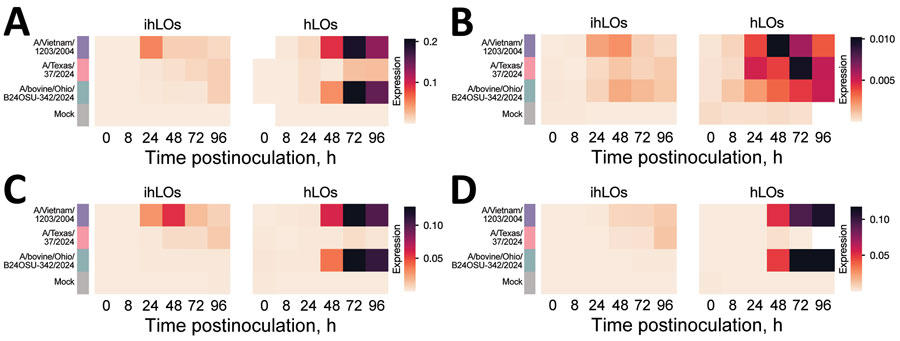
Figure 3. Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines in a comparison of contemporary and historic highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus replication in human lung organoids. A) interferon β; B) tumor necrosis factor α; C) interleukin (IL) 6; D) IL-1β. iPSC-derived human lung organoids (ihLO) or adult-derived human lung organoids (hLO) were infected as described in [[ANCHOR###F1###Figure 1###Anchor]]. We infected ihLO and hLO as described in [[ANCHOR###F1###Figure 1###Anchor]]. We extracted RNA from 2.5 × 104 cells by using the QIAGEN RNeasy kit (QIAGEN, https://www.qiagen.com), following the tissue extraction instructions. We ran quantitative reverse transcription PCR by using primers (Integrated DNA Technologies, https://www.idtdna.com) to detect proinflammatory cytokines. Data were normalized to an internal control (ACTB), and expression was calculated using the 2–ΔCt method, due to limited detection of proinflammatory cytokines in mock-infected samples. White cells indicate samples where PCR amplification was not detected. Mean expression for 6 ihLO and 3 hLO biologic replicates is shown. hLOs, adult stem cell–derived human lung organoids; ihLO, iPSC-derived human lung organoids; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.