Volume 31, Number 4—April 2025
Research
Attribution of Salmonella enterica to Food Sources by Using Whole-Genome Sequencing Data
Figure 2
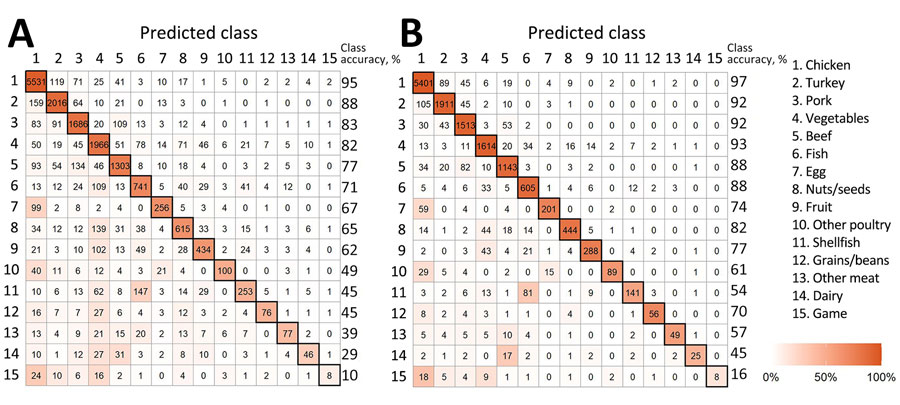
Figure 2. Confusion matrix from the random forest model trained on Salmonella isolates collected from single food categories in the United States and other countries during 2003–2018 and 613 isolates collected before 2003. A) Confusion matrix for all Salmonella isolates from single food categories (N = 18,661). B) Confusion matrix from the random forest model for Salmonella isolates from single food categories with a maximum predictive probability of >0.50 (n = 14,888).
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: March 02, 2025
Page updated: March 24, 2025
Page reviewed: March 24, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.