Rabbit Hepatitis E Virus, Ukraine, 2024
Sérgio Santos-Silva, Yevheniia Dudnyk, Oksana Shkromada, Maria S.J. Nascimento, Helena M.R. Gonçalves, Wim H.M. Van der Poel, António Rivero-Juarez, and João R. Mesquita

Author affiliation: School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal (S. Santos-Silva, J.R. Mesquita); Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Sumy National Agrarian University, Sumy, Ukraine (Y. Dudnyk, O. Shkromada); Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Porto, Porto (M.S.J. Nascimento); Faculty of Sciences, University of Porto, Porto (H.M.R. Gonçalves); Wageningen University, Lelystad, the Netherlands (W.H.M. Van der Poel); Wageningen Bioveterinary Research, Lelystad (W.H.M. Van der Poel); Hospital Universitario Reina Sofia, Instituto Maimonides de Investigación Biomédica de Córdoba, Universidad de Córdoba, Cordoba, Spain (A. Rivero-Juarez); Center for Biomedical Research Network in Infectious Diseases, Health Institute Carlos III, Madrid, Spain (A. Rivero-Juarez); Center for the Study of Animal Science, Institute of Sciences, Technologies, and Agroenvironment, University of Porto, Porto (J.R. Mesquita); Associate Laboratory for Animal and Veterinary Science (AL4AnimalS), Lisbon, Portugal (J.R. Mesquita)
Main Article
Figure
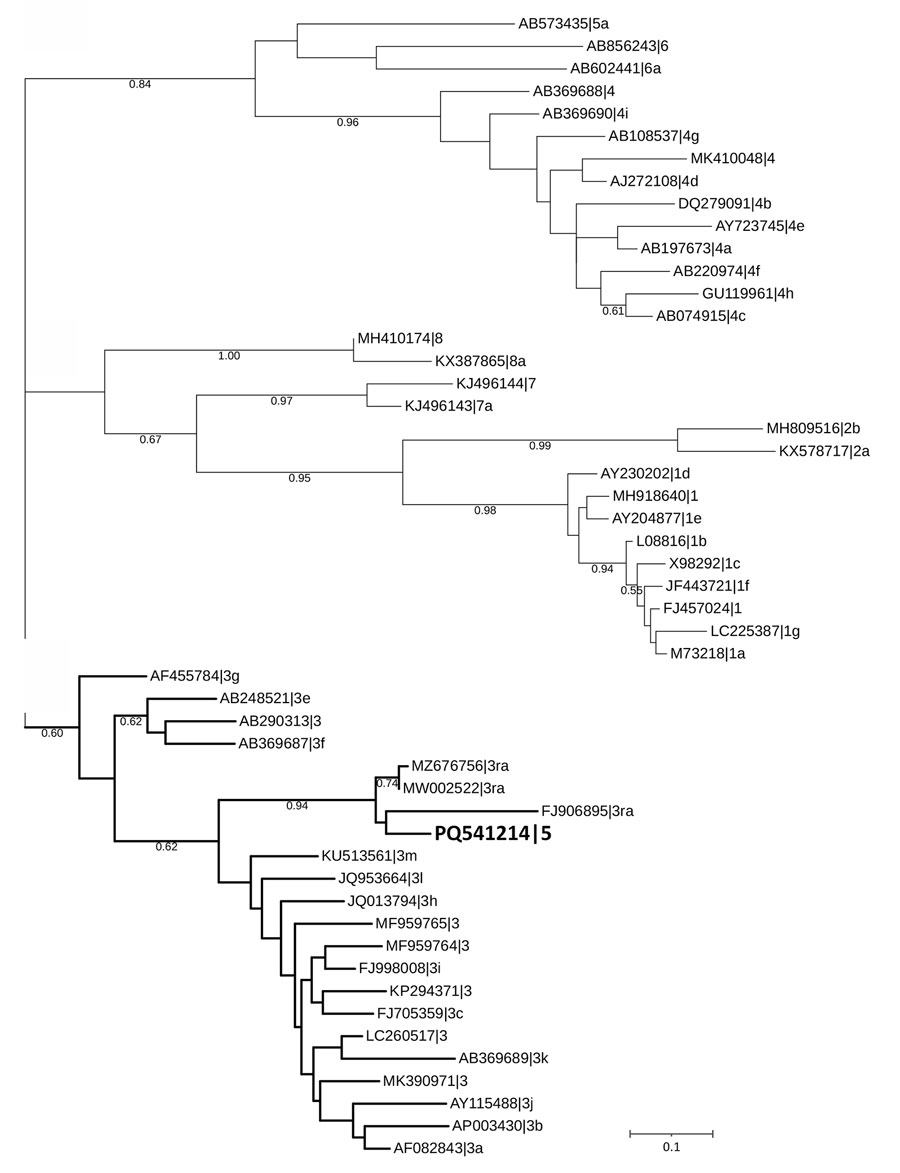
Figure. Phylogenetic tree of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase sequence of rabbit hepatitis E virus (HEV), Ukraine, 2024. Bold indicates the HEV sequence identified in this study. The tree was inferred using MEGA X software (https://www.megasoftware.net) with the Kimura 2-parameter substitution model and visualized using the Interactive Tree of Life (https://itol.embl.de). The tree includes 51 HEV nucleotide sequences, with reference sequences retrieved from GenBank, displayed with their accession number, genotype, and subgenotype. The tree is structured into distinct clusters corresponding to different HEV genotypes and subgenotypes; the detected sequence groups within the HEV-3ra cluster. This placement indicates its close relationship to previously reported rabbit HEV sequences. Sequence analysis confirmed the genome identity as HEV. The ORF2 fragment (GenBank accession no. PQ541216) showed identity with 2 human sequences from Switzerland: 92.04% identity with GenBank accession no. OX044324 and 91.72% with GenBank accession no. OV844765. One ORF1 fragment (GenBank accession no. PQ541214) showed identity with rabbit sequences from Australia: 91.42% with GenBank accession no. MW002522 and 90.99% with GenBank accession no. MZ676756. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Main Article
Page created: February 04, 2025
Page updated: March 24, 2025
Page reviewed: March 24, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
